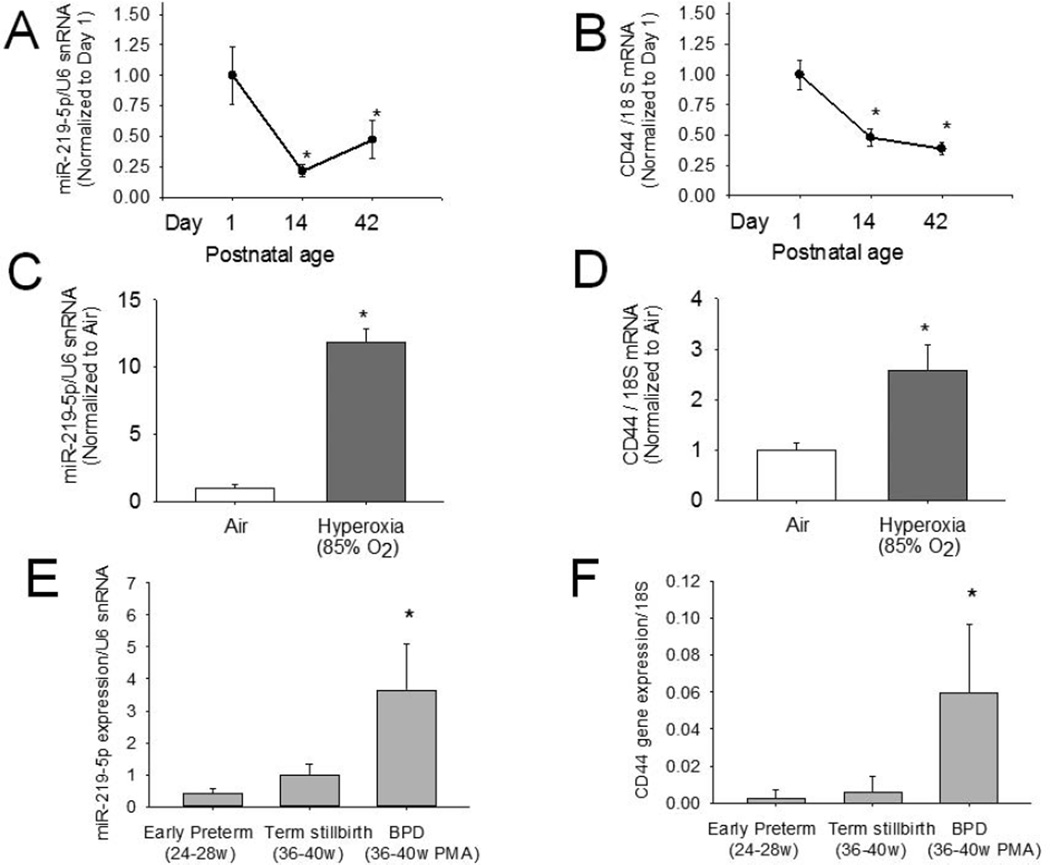
Figure 2.
Evaluation of miR-219 and CD44 in a newborn mouse model (Panels A-D) and in human lung (Panels E-F). Lung miR-219 (Panel A) and CD44 mRNA (Panel B) decreased during alveolar septation, with expression on postnatal days 14 and 42 significantly less as compared with day 1; *p<0.05. Lung miR-219 (Panel C) and CD44 mRNA (Panel D) were also increased on postnatal day 14 during hyperoxia exposure (*p<0.05 compared with air). Lung miR-219 (Panel E) and CD44 mRNA (Panel F) were increased in human lungs with BPD as compared to early preterm or term stillbirth lungs (Mean±SEM; n=4/group)