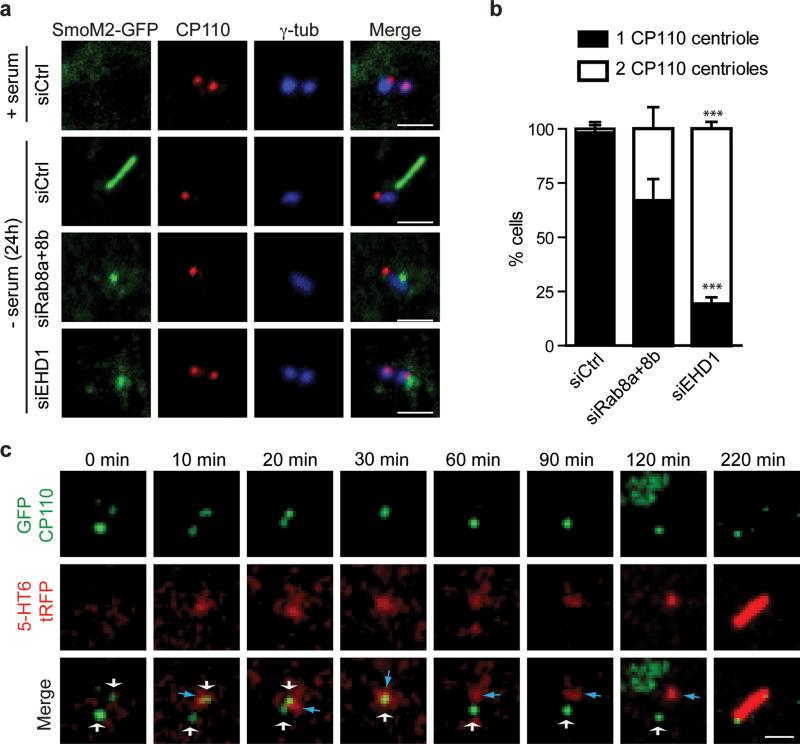
Figure 6. EHD1-dependent ciliary vesicle formation stimulates CP110 loss from the distal end of the mother-centriole.
a. RPE SmoM2-GFP cells treated with siRNA for 72h, grown in serum or serum starved for the last 24h, and stained with anti-CP110 and anti-γ-tubulin antibodies. Scale bar: 2 μm.
b. Quantification of serum starved RPE cells described in (a) showing CP110 localization on the mother and daughter centriole (2 dots) or only the daughter centriole (1 dot). Note that we disregarded cells with more than 2 dots in our quantification. Means ± SD are pooled data from 3 independent experiments with n=6 areas imaged (total number of cells counted in all experiments: siCtrl, 184; siRab8a+8b, 161; siEHD1#1, 157). Two tailed t-test analysis compared with siCtrl, *** P<0.0001. Statistics source data can be found in Supplementary Table 2.
c. RPE cells transiently co-expressing GFP-CP110 and 5-HT6-tRFP, serum starved for 1h and imaged live over time by spinning disk confocal microscopy as in Fig 5c. Representative images of maximum intensity projections of z-stack imaging series from 5 cilia assembly events observed. White and blue arrows indicate CP110-positive centrioles and 5-HT6 vesicles respectively. For presentation purposes images were smoothed with a Gaussian blur filter. Scale bar: 2 μm.