Figure 1.
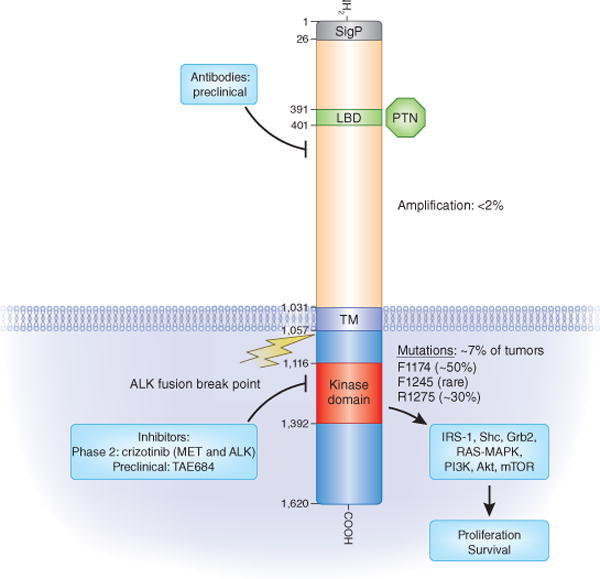
The ALK receptor kinase: its domains, pathways, mutations and inhibitors. The different domains of ALK are shown within their bordering amino-acid positions. The major mutations found by Mossé et al.4, Janoueix-Lerosey et al.5, Chen et al.6 and George et al.7 in the kinase domain and their relative frequencies (somatic or germline) are shown. The percentage of tumors that show ALK amplification or contain ALK mutations is indicated. Representative small-molecule kinase inhibitors that also inhibit ALK are listed according to their current status. The ALK breakpoint that leads to fusion proteins in different cancers is indicated. SigP, signal peptide; LBD, ligand binding domain; PTN, pleiotrophin; TM, transmembrane domain; IRS-1, insulin receptor substrate 1; Grb2, growth factor receptor–bound protein-2; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin.
