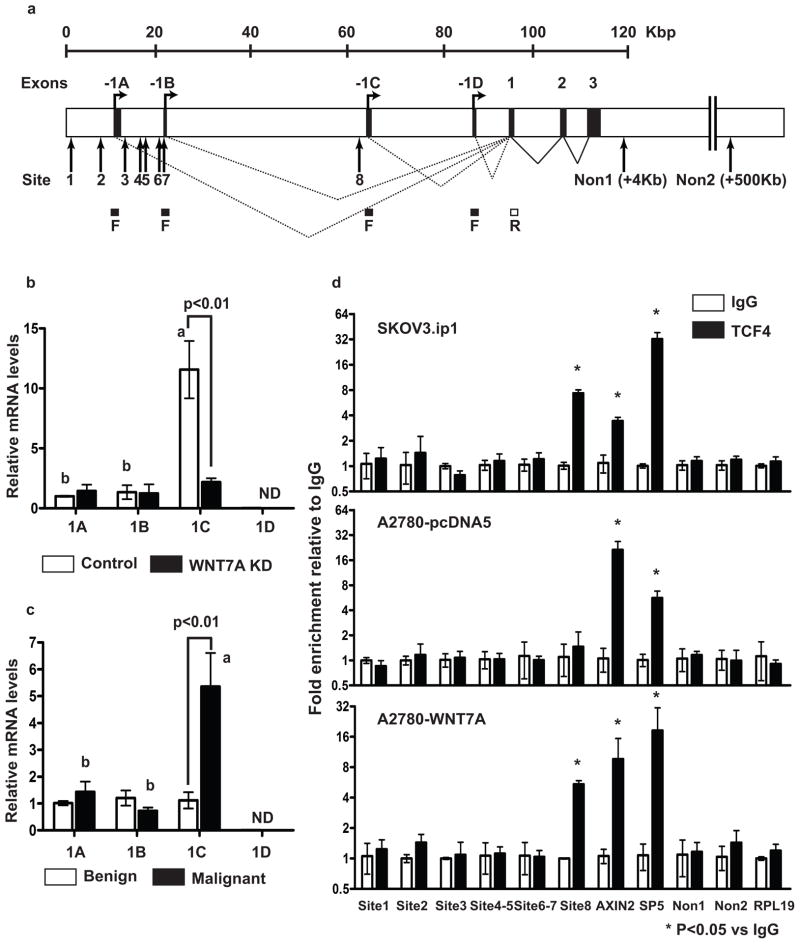
Figure 3.
FGF1 is a direct β-catenin/TCF target. (a) Human FGF1 gene and transcripts. Alternative splicing of untranslated exons (1A, 1B, 1C and 1D) to exon 1 will generate mRNAs 1A, 1B, 1C and 1D. A total of 8 consensus TCF/LEF-binding elements (WWCAAWG, W=A/T) at the FGF1 genomic locus are shown. F; forward primers designed in 1A, 1B, 1C or 1D and R; reverse primer designed in exon 1. Relative FGF1 alternative splicing mRNA levels in (b) control and WNT7A knockdown SKOV3.ip1 cells, and (c) human ovarian normal/benign (n=5) and malignant (n=36) tumors. Different letters denote transcripts that have statistically significant (P<0.01) differences in mean expression levels. ND: non detectable. (d) ChIP assay of DNA isolated from SKOV3.ip1, A2780-pcDNA5 and WNT7A overexpressing cells immunoprecipitated with TCF4 antibody. Immunoprecipitated DNA was analyzed by qPCR and normalized to input. TCF4 binding sites at AXIN2 and SP5 loci were used as positive controls. Three irrelevant non TCF4 binding sites on the same chromosome of FGF1 and different chromosome at the RPL19 locus were used as negative controls.