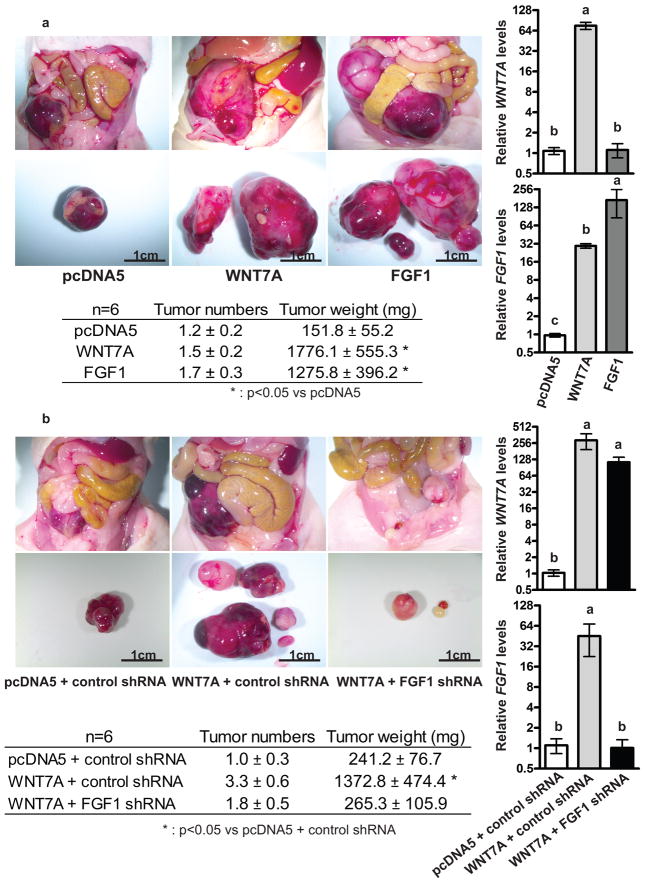
Figure 4.
FGF1 promotes the tumorigenic functions of WNT7A. (a) WNT7A or FGF1 overexpression increased tumor growth. Nude mice were injected i.p. with vector control cells, WNT7A overexpressing, or FGF1 overexpressing cells. The images provide a direct view of the abdominopelvic cavity and tumors isolated from mice. Total tumor numbers and weight 5 weeks after i.p. injection are shown (n=6 each group). Relative WNT7A or FGF1 expression in orthotopic tumors that developed from vector control, WNT7A overexpressing, or FGF1 overexpressing cells. Different letters denote groups that have statistically significant (P<0.05) differences in mean expression levels. (b) FGF1 knockdown inhibits WNT7A-dependent tumor growth. FGF1 knockdown in WNT7A overexpressing cells inhibited tumor growth. Nude mice were injected i.p. with vector control, or control or FGF1 knockdown WNT7A overexpressing cells. The images provide a direct view of the abdominopelvic cavity and tumors isolated from the mice. Total tumor numbers and weight 5 weeks after i.p. injection are shown (n=6 each group). Relative WNT7A or FGF1 expression in orthotopic tumors that developed from vector control, or control or FGF1 knockdown WNT7A overexpressing cells. Different letters denote groups that have statistically significant (P<0.05) differences in mean expression levels.