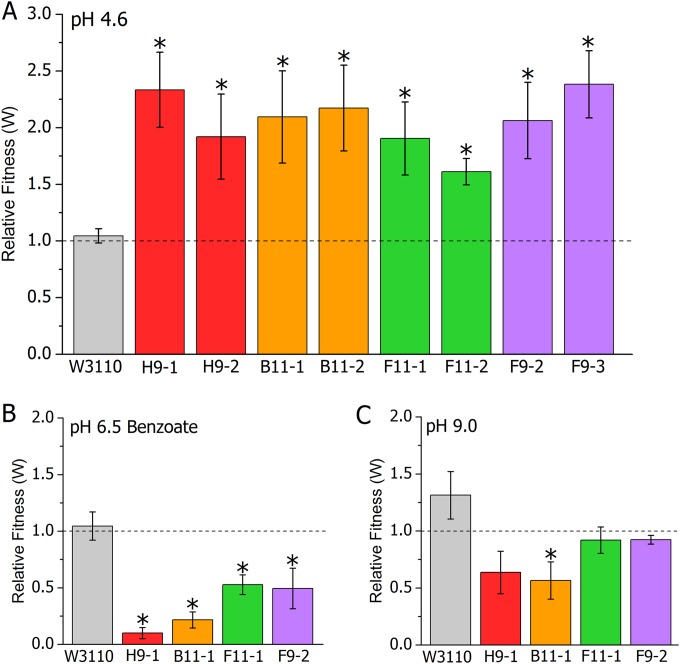
FIG 2.
Fitness changes in acid-evolved clones. For each pair of strains, the relative fitness (W) was calculated as described in Materials and Methods. To control for any fitness effect of the transduced lac-negative allele, the original lac+ ancestral wild type was cocultured with the lac-negative wild type (gray bars). (A) pH 4.6. Clones were serially diluted (1:200) in LBKmal buffered to pH 4.8 and incubated overnight twice prior to each experiment. Each isolate was then cocultured with a lac-negative variant of the ancestral wild type (or else the lac-negative isolate was cocultured with a lac+ ancestor) for 24 h in LBKmal buffered to pH 4.6. Error bars represent SEMs (n = 6 for evolved strains, n = 18 for ancestral strain W3110). (B) Benzoate. Strains were serially diluted 1:200 and incubated overnight twice in LBK medium buffered to pH 6.5. For the competition, each isolate and ancestor were cocultured for 24 h in LBK medium with 15 mM benzoic acid buffered with 100 mM PIPES at pH 6.5 (n = 4 for evolved strains, n = 8 for W3110) (C) pH 9.0. Strains were serially diluted and incubated overnight twice in LBK medium buffered to pH 8.5. For the competition, each isolate and ancestor were cocultured for 24 h in LBK medium buffered with 150 mM TAPS at pH 9.0 (n = 4 for evolved strains, n = 8 for W3110). *, P ≤ 0.05 (t test) in comparison with the results for W3110.