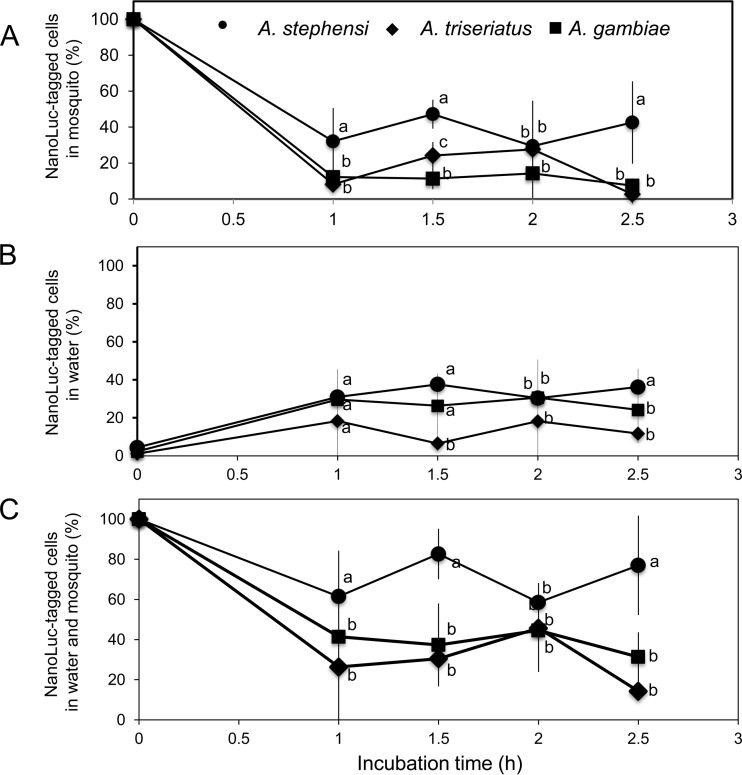
FIG 2.
Digestibility analysis of E. anophelis by Aedes triseriatus, A. gambiae, and A. stephensi larvae. (A) Larval mosquitoes fed SCH814 cells were pooled (4 at each time point), homogenized, washed, and subjected to the NanoLuc activity assay. Cell densities at the different time points were normalized to the initial cell densities in corresponding mosquitoes at time zero. (B) Cells in the water were sampled, washed with PBS by centrifuging, resuspended in PBS, and subjected to the NanoLuc activity assay. Cell densities at the different time points were normalized to the initial cell densities at time zero. (C) The NanoLuc-tagged cells recovered from mosquitoes and water samples were quantified and normalized to those at time zero. Values are means ± standard deviations; triplicate experiments were performed. Significant differences among Aedes triseriatus, A. gambiae, and A. stephensi samples at each time point were determined by using PROC GLM. Different letters (a, b, and c) indicate significant differences in NanoLuc-tagged cell densities among these samples at each time point (P < 0.05). Means with the same letters indicate that no statistically significant difference was observed for these samples (P > 0.05).