FIGURE 6.
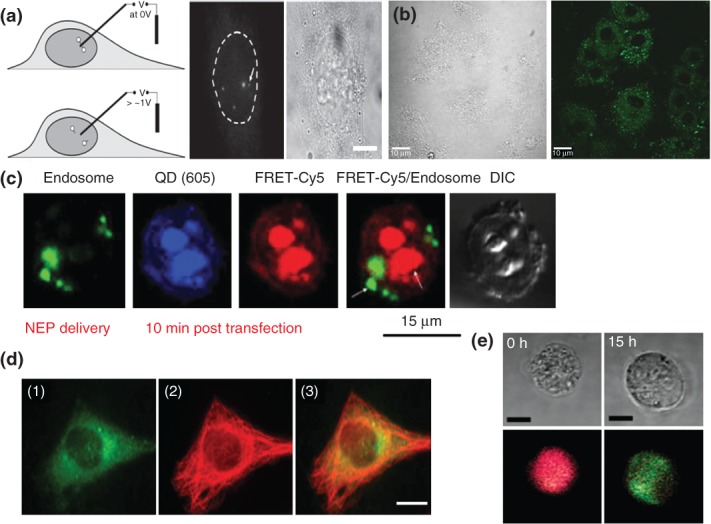
Active cellular quantum dot (QD) delivery. (a) Electrochemically controlled deconjugation for QD delivery to the nucleus. A boron nitride nanoneedle bearing streptavidin-coated QDs attached to a SAM layer are desorbed when a voltage is applied (left panel) which allowed for single QD tracking within the nucleus of a live HeLa cell (split right panel). The nucleus is denoted with the dashed line (left) alongside the brightfield image (right). Scale bar, 1 µm. (Reprinted with permission from Ref 88. Copyright 2010 Wiley) (b) Reversible permeabilization facilitates cellular QD entry. The 530 nm-emitting CdSe/ZnS QDs delivered intracellularly using combination of osmotic fluid transport and membrane-permeabilizing saponin. Image shows DIC (left) and QD (right) signal in H9C2 rat cardiomyocyte cells. (Reprinted with permission from Ref 89. Copyright 2013 IOP Publishing) Scale bar, 10 µm. (c) Nanochannel electroporation (NEP) transfection of QD-antisense-lipoplex assemblies monitored by Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET). NEP transfection of lipoplex NPs containing QDs delivers lipoplexes directly to the cytosol within 10 min in A549 cells. Note the QD (blue) and Cy5-antisense (red) signals are matched and separate from the endosomal label (green). QD-Cy5 FRET was used to monitor the dissolution of the QDs and Cy5-labeled antisense oligonucleotide from the assemblies over time. (Reprinted with permission from Ref 90. Copyright 2013 Wiley) (d) Nanoblade-mediated labeling of cytoskeleton with tubulin-QD conjugates. Laser-induced surface plasmons from a titanium-coated capillary induced transient pores in the plasma membrane allowing the intracellular influx of tubulin-QD conjugates (green, panel 1) that incorporate into the cytoskeletal network. Immuno-counterstaining of the tubulin network (red, panel 2) and merged images (panel 3) are shown to illustrate the high degree of overlap. Scale bar, 10 µm. (Reprinted with permission from Ref 91. Copyright 2012 ACS) (e) Microfluidic device-mediated cytosolic delivery of QD-dye FRET constructs. A QD-Rhodamine donor–acceptor pair joined by a glutathione-sensitive dithiol linkage is delivered to the cytosol via microfluidic-driven cellular deformation initially shows full energy transfer of the green QD to the red dye (0 h, red color, left panel). After 15 h, the cytosolic glutathione reduces the thiol linkage resulting in reemission of the QD donor (15 h, green color, right panel). Scale bar, 10 µm. (Reprinted with permission from Ref 92. Copyright 2012 ACS)
