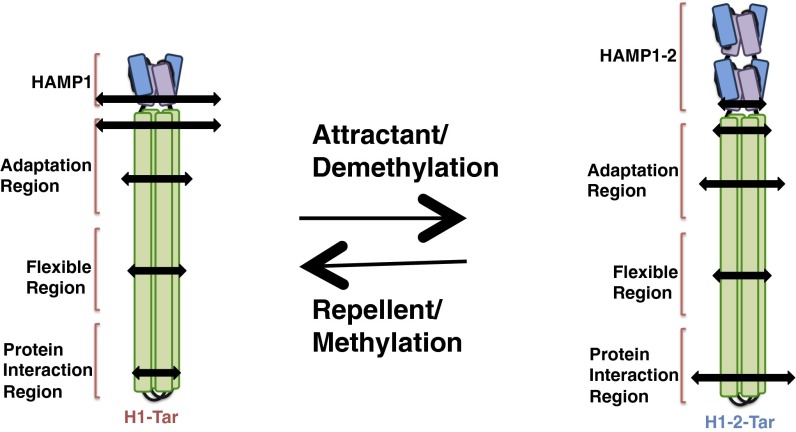
Fig. 6.
Dynamical properties of the HAMP KCM. The HAMP and PIR show opposing dynamical properties depending on receptor activation state (length of arrow correlates with conformational breadth). Activating HAMP or increased modification produces a dynamic HAMP and static CheA/CheW-coupling tip. In contrast, an inhibitory HAMP or decreased modification produces a conformationally stable HAMP but dynamic CheA/CheW-coupling tip. Inversion of dynamics occurs at the Gly hinge, which does not change properties in any of the states tested.