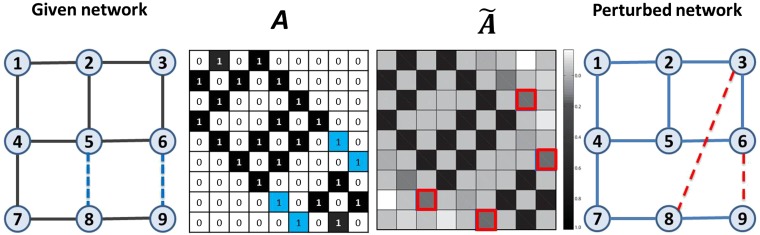
Fig. 1.
An illustration of how to calculate the structural consistency. In the first plot, the blue dashed links constitute the perturbation set (corresponding to ), while the solid links constitute the set (corresponding to ). The second plot shows the adjacency matrix A of the given network, where the number in each square is the corresponding value of the matrix element. The black and blue squares represent the links in and , respectively. To calculate the consistency, we perturb with . The perturbed matrix is shown in the third plot, from which we derive the perturbed network in the fourth plot, where the red dashed lines are outcome links selected by ranking all links in in descending order according to their corresponding values in . Since there are two links in , then , and the set . In this case, only one of the two blue links is recovered by perturbation; then we have .