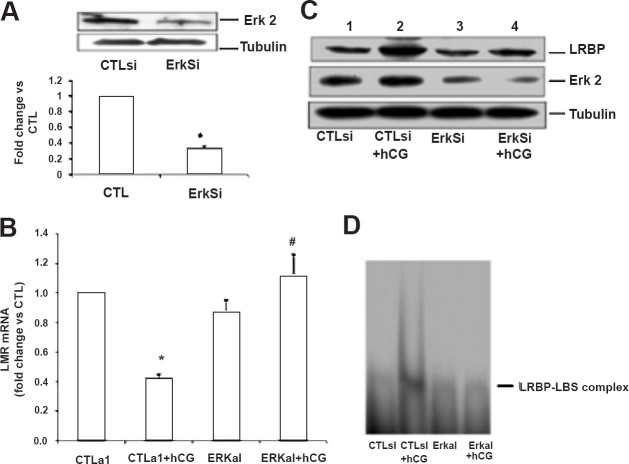
Fig. 5.
ERK1/2 silencing inhibits hCG-induced decrease in LHR mRNA levels and increases in LRBP protein expression and binding activity. Granulosa cells were transfected with either control siRNA (CTLsi) or ERK 1/2 siRNA (ERKsi) and cultured for 48 h. After serum-starving for another 24 h, cells were treated with hCG (10 IU/ml) for 12 h and processed for total RNA isolation, for Western blot analysis, or for REMSA. A. ERK1/2 silencing was confirmed by the Western Blot analysis of cell lysates using total ERK2 antibody. B. Total RNAs were reverse transcribed, and the resulting cDNAs were subjected to real-time PCR quantitation using LHR-specific primers and probes. The graph represents changes in mRNA levels normalized to 18S rRNA and are shown as fold change vs. control. Error bars, mean ± SE.*, P < 0.05 vs. CTL; #, P < 0.05 vs. hCG; n = 3. C. Cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis to detect LRBP using specific antibody. The same membranes were then stripped and reprobed for ERK2 and β-tubulin. The blot shown is a representative of three independent experiments. D. G el mobility shift analysis was performed with [32P]-labelled rat LBS (1.5 × 105 cpm) and S100 fractions containing equal amounts of total protein extracted from the different treatment groups. The autoradiogram shown is representative of three independent experiments. (Source: Ref. 27, Reproduced with permission).