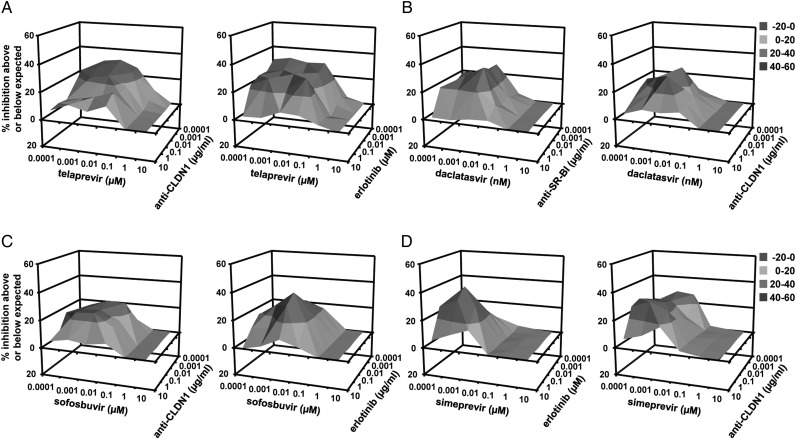
Figure 7.
Synergistic effect of combining direct-acting antivirals and entry inhibitors in treatment of HCV infection using persistently infected DMSO-differentiated hepatoma cells. HCV-infected cell culture was established by transfecting RNA encoding wild-type HCV Luc-Jc1 into Huh7.5.1 cells. The cells were then differentiated in the presence of 1% DMSO for 5 days before treatment with the combinations of (A) telaprevir+anti-CLDN1 mAb (left) or erlotinib (right), (B) daclatasvir+anti-SR-BI mAb (left) or anti-CLDN1 mAb (right), (C) sofosbuvir+anti-CLDN1 mAb (left) or erlotinib (right), (D) simeprevir+erlotinib (left) or anti-CLDN1 mAb (right). HCVcc infection was assessed by luciferase activity 5 days after treatment. Synergy was assessed using the Prichard and Shipman method.25