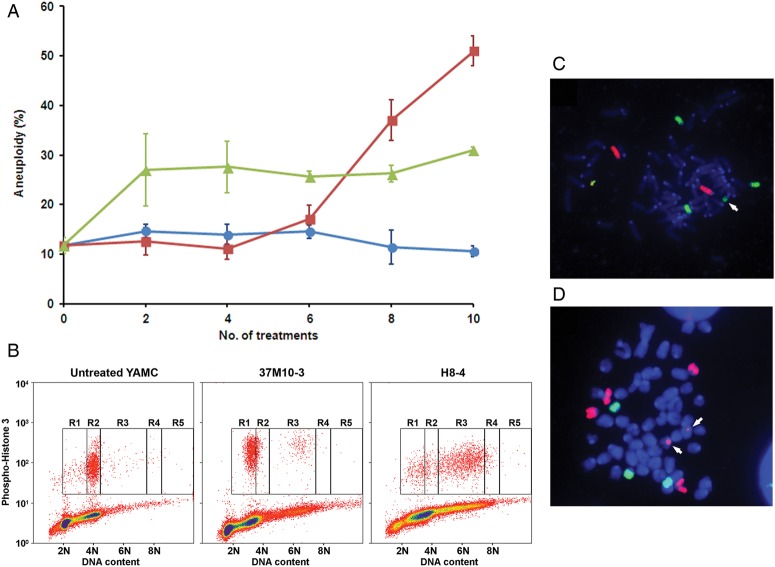
Figure 2.
Enterococcus faecalis-infected macrophages and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE) induce aneuploidy and chromosomal instability (CIN) in primary colon cancer cells. (A) After 8 weekly treatments, the rate of aneuploidy significantly increases in YAMC cells co-cultured with E. faecalis-infected macrophages (red squares) compared with untreated control (blue circles). The proportion of aneuploid cells increases after only two treatments with 1 µM 4-HNE (green triangles). (B) Representative histograms of mitotic cells by fluorescent-activated cell sorting show increased numbers of aneuploid cells (R1 and R3 windows) in YAMC clones isolated after 10 treatments with E. faecalis-infected macrophages (37M10-3, middle) and 8 treatments with 4-HNE (H8-4, right) compared with sham-treated cells (left). (C) and (D), fluorescence in situ hybridisation analysis shows aberrant karyotypes with chromosomal translocations (arrows). Red, chromosome 11; green, chromosome 18.