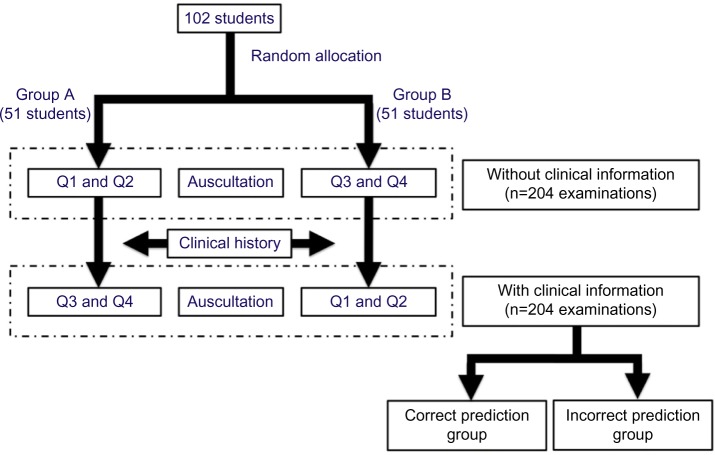
Figure 1.
Outline of the study.
Notes: One hundred and two students were randomized to Group A (51 students) that started with question (Q)1 and Q2 or Group B (51 students) that started with Q3 and Q4. The students initially performed auscultation without clinical information (n=204 examinations, 51 students ×2 questions ×2 groups), and then performed auscultation again after being given a history (n=204 examinations, 51 students ×2 questions ×2 groups). The students were then classified into correct or incorrect prediction groups, depending on whether correct or incorrect diagnoses were predicted from the clinical information, respectively.