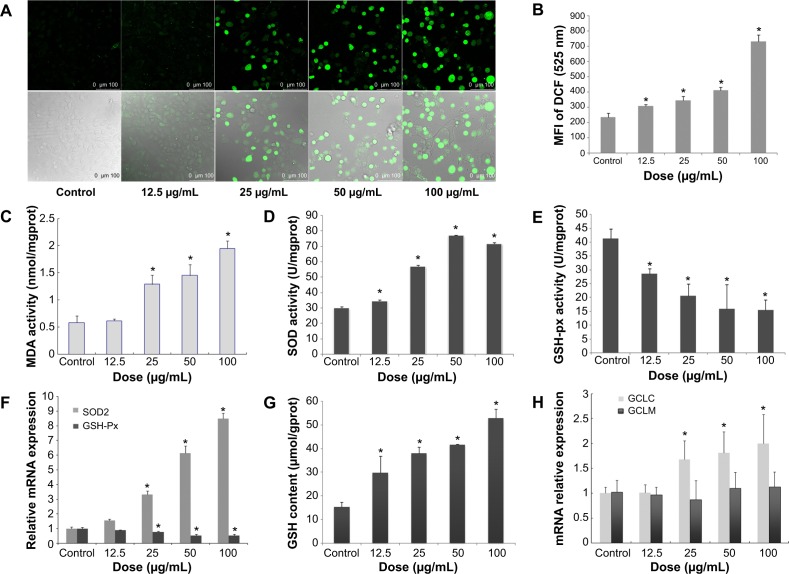
Figure 3.
Oxidative stress and damage induced by SiNPs in HUVECs.
Notes: *P< 0.05 versus control. Data expressed as means ± SD from three independent experiments. HUVECs were treated with increasing concentrations of SiNPs for 24 hours, and then the fluorescence intensity of DCF was measured using laser scanning confocal microscopy and flow cytometry. The intracellular levels of ROS were significantly increased in a dose-dependent manner (A, B), and so was the production of MDA (C). SOD activity was increased, while GSH-Px levels decreased significantly in a dose-dependent way (D, E). Meanwhile, the relative mRNA expression of SOD2 and GSH-Px were measured by quantitative real-time PCR. Significant changes in their mRNA expressions were observed, which was consistent with the corresponding change in their activities (F). Additionally, GSH content increased, induced by SiNPs, and the relative mRNA expression of GCLC normalized to β-actin was upregulated, but there was no significant change in that of GCLM (G, H). In figure A the upper images were DCFH-DA staining under confocal microscopy. The lower images were DCFT-DA staining merged with optical morphology at the same visual field.
Abbreviations: HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; SiNPs, silica nanoparticles; SD, standard deviation; DCF, dichlorofluorescein; ROS, reactive oxygen species; MDA, malondialdehyde; GSH-Px, glutathione peroxidase; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; mRNA, messenger ribonucleic acid; DA, diacetate; SOD, superoxide dismutase; GCLC, glutamate cysteine ligase – catalytic; GCLM, glutamate cysteine ligase – modifier.