Figure 6.
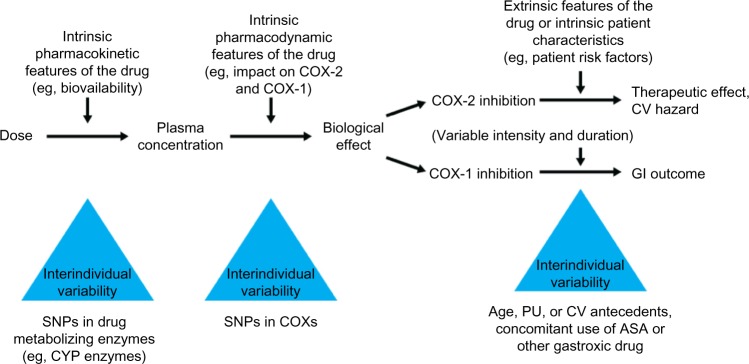
Determinants and sources of variability in the individual response to an NSAID.
Notes: There are a number of factors that influence the likelihood of experiencing GI or CV adverse events associated with NSAID use. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the drug may be affected by genetic factors (eg, differences in expression of drug-metabolizing enzymes). In addition, individual clinical and demographic characteristics may affect the therapeutic activity and tolerability of the NSAID. Adapted with permission from Patrono C, Patrignani P, García Rodríguez LA. Cyclooxygenase-selective inhibition of prostanoid formation: transducing biochemical selectivity into clinical read-outs. J Clin Invest. 2001;108(1):7–13. Permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.31
Abbreviations: ASA, acetylsalicylic acid; COX, cyclooxygenase; CV, cardiovascular; CYP, cytochrome enzymes; GI, gastrointestinal; NSAID, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug; PU, peptic ulcer; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism.
