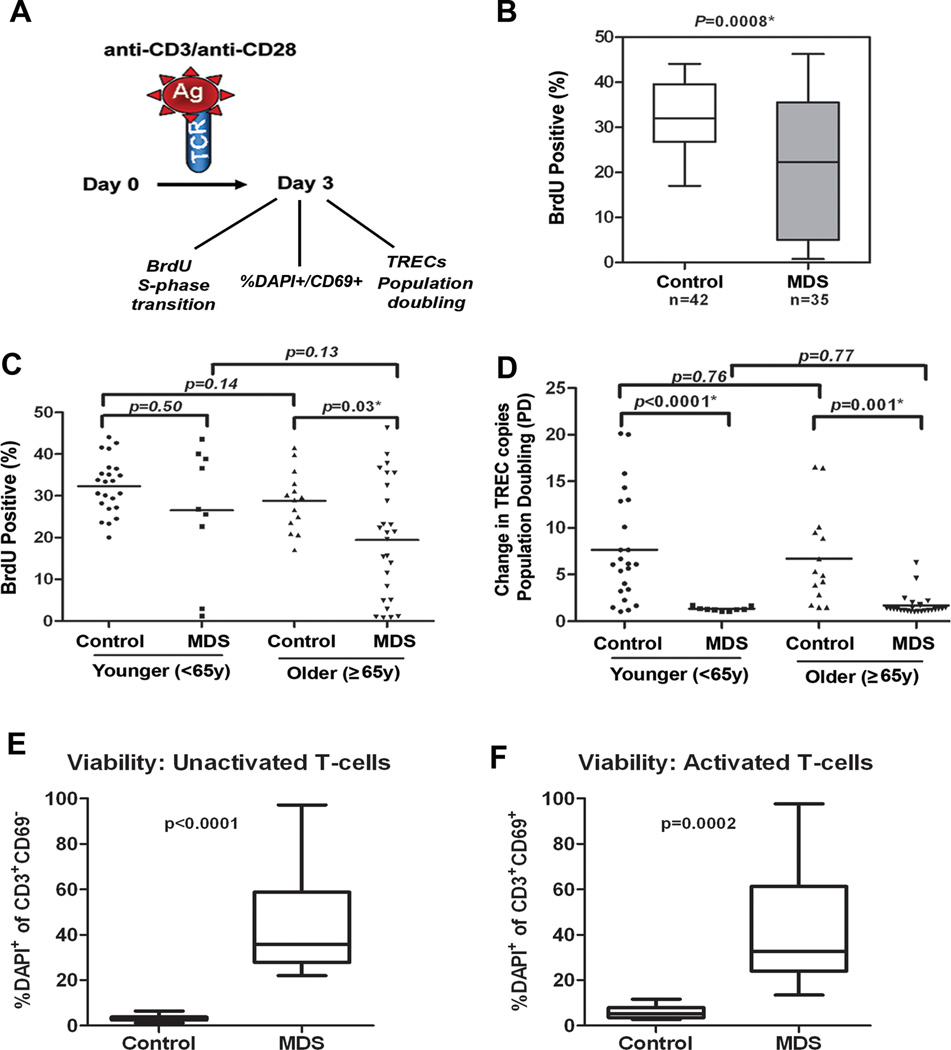
Figure 2. Deficiency of the proliferative capacity of CD3+ T-cells in MDS patients.
CD3+ T-cells were negatively separated from blood of MDS patients (n=35) and healthy donors (n=42) and samples were divided into two aliquots. One aliquot was used for assays on day 0 and the other stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 beads for 3 days. (A) Shows a diagram of the analyses conducted. On day 0 cells were used for TREC baseline measurements, stained with CFSE and examined for DAPI on CD69+ cells (as defined in supplemental material). On day 3, BrdU incorporation was measured by flow cytometry to determine the percentage of T-cells capable of entering S-phase in MDS patients and healthy donors after stimulation. Samples were also collected for TREC DNA content, % DAPI within the CD69+ population and for CFSE dilution assays (as defined in supplemental material). (B) BrdU indicates the percentage of cells capable of entering S-phase. The box and whisker plots of data are shown for 42 controls and 35 MDS patients. (C) BrdU data divided into groups of younger and older patients and controls based on age <65y and ≥65y. (D) Dilution of the number of TRECs per cell indicates the replication potential. Population doubling (PD, ie, replication potential) was calculated as the ratio of the TREC DNA copy number per cell in unstimulated T-cells and stimulated T-cells on day 3 after antiCD3/CD28 stimulation. Case-control difference in PD analyzed in groups based on age<65y and ≥65y. Case-control differences in BrdU and PD in purified CD3+ T-cells were compared using the Wilcoxon signed rank. (E) percentage of DAPI+CD69+ cells in unactivated T-cells at baseline (Time 0) and the (F) percentage of these cells after activation in MDS patients and control. P-values based on Wilcoxon test for the case-control differences are shown at the top of each panel. Log-transformed values were then used in multivariate logistic regression analyses to adjust for age (as continuous variable) and sex, and the case-control. Exemplary CFSE staining in a control and case sample and summary of data in 6 donors tested is shown in supplementary Figure 2 and confirm deficiency in population doubling. All tests were two-sided and associations were considered statistically significant at a significance level of p<0.05.