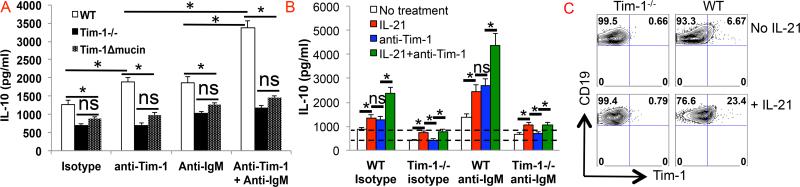
Figure 2. Tim-1 and BCR or IL-21 signaling together strongly promoted B cell IL-10 production while a defect in Tim-1 signaling in B cells reduced IL-10 production.
Purified splenic CD19+ B cells from 2-3 month-old WT, Tim-1Δmucin or Tim-1−/− mice were cultured in the presence of anti-Tim-1 (clone 5F12), (Fab’)2 fragment anti-IgM or both without (A) or with IL-21 (B). After 3 days, IL-10 production in culture supernatants was measured by ELISA. * P < 0.01; ns, not significant. C) Representative flow cytometry plots showing Tim-1 expression by splenic CD19+ B cells from WT and Tim-1−/− mice after 3-day culture in the presence of IL-21. n ≥ 3 per group.