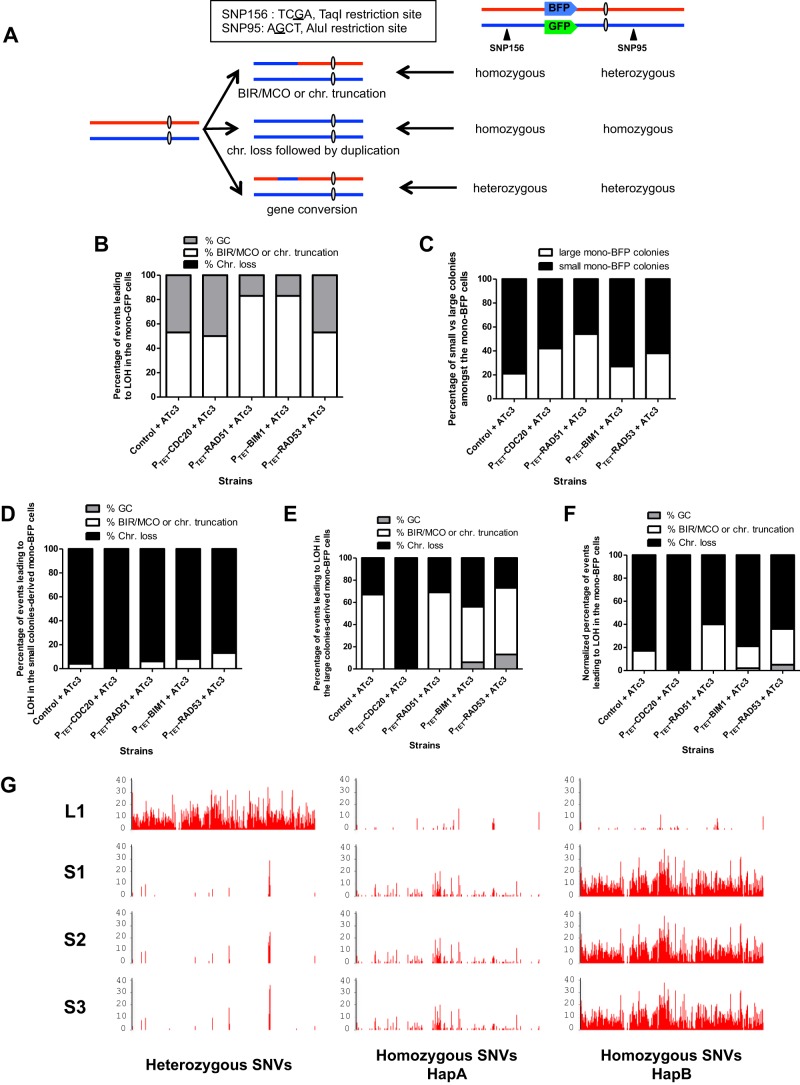
Fig 3.
SNP typing reveals a shift in the molecular mechanisms leading to LOH upon the overexpression of some of the candidate genes. (A) Map of Ch4 and localization of the BFP-GFP system. The SNPs used for RFLP characterization are indicated by black triangles. Telomere-proximal SNP 156 is part of a TaqI restriction site. One allele contains the TaqI site, while the other does not. Centromere-proximal SNP 95 is located in the middle of an AluI restriction site. One allele contains the AluI site, while the other does not. The heterozygosity status of these SNPs provides information on the molecular mechanisms that give rise to LOH. chr., chromosome. (B) SNP-RFLP typing of Bfp− Gfp+ cells. The histogram shows the proportion of MCO/BIR or chromosome truncation versus chromosome loss in the Bfp− Gfp+ population. MCO/BIR or chromosomal truncation events correspond to isolates that have maintained a heterozygous SNP 95 and displayed a homozygous SNP 156. Chromosome loss events correspond to isolates in which both SNPs 95 and 156 became homozygous. Gene conversion events correspond to isolates in which both SNPs 95 and 156 remained heterozygous. (C) Proportion of small versus large colonies giving rise to true mono-BFP cells. (D) SNP-RFLP typing of small-colony-derived Bfp+ Gfp− cells. (E) SNP-RFLP typing of large-colony-derived Bfp+ Gfp− cells. (F) SNP-RFLP typing of Bfp+ Gfp− cells. The normalized percentage of each molecular mechanism, for instance, gene conversion, was calculated as follows: normalized % GC = (% small colonies × % GC in small colonies) + (% large colonies × % GC in large colonies). (G) Heterozygous and homozygous SNV density maps of one large- and three small-colony-derived cells that have undergone LOH at the BFP-GFP locus of Ch4. The number of heterozygous SNVs in each 10-kb region along Ch4 was computed and is shown, revealing LOH by gene conversion in the large-colony-derived cells and by chromosome loss and reduplication on Ch4 in the small-colony-derived cells. Sequencing reads were mapped on the HapA or HapB reference sequence and yielded similar heterozygous SNP density maps. Only the result of mapping on HapB is shown (left). The number of homozygous SNVs in each 10-kb region along HapA (middle) or HapB (right) was computed and is shown. The high density of homozygous SNVs upon mapping on HapB indicates that chromosome loss in small-colony-derived cells affected Ch4B.