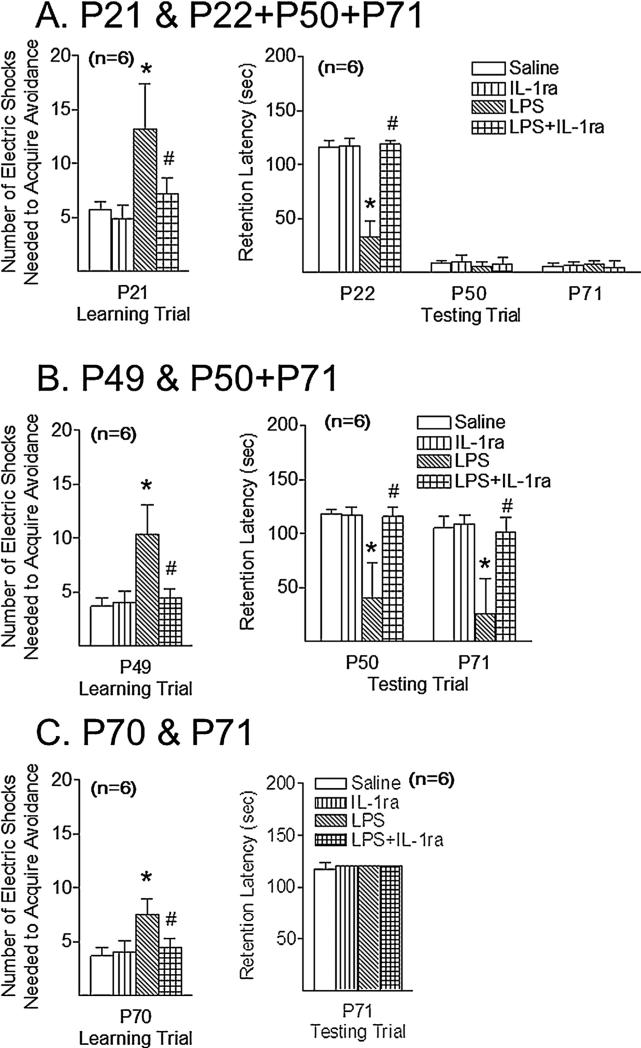
Fig. 1.
IL-1 receptor antagonist attenuated the LPS exposure-induced learning and memory deficit, as determined by passive avoidance, 16 (P21) (A), 44 (P49) days (B), and 65 days (P70) (C) after the injection. Three group of experiments were performed: (A) learning trial at P21 juvenile rats; (B) learning trial at P49 adolescent rats; (C) learning trial at P70 adult rats. The results are shown as the number of electric foot shocks required to retain the rat on the safe board (left panel) and the retention latency to step down from the board on the next day or longer (right panel). The results are expressed as the mean±SD of six animals in each group and analyzed by the two-way ANOVA (learning, left panel) or the two-way repeated measures ANOVA for data from tests conducted continuously at different postnatal days (memory, right panel), followed by the Student– Newman–Keuls test. *p < 0.05 represents significant difference for the LPS group as compared with the saline group on the same postnatal day. p < 0.05 represents significant difference for the LPS + IL-1ra group as compared with the LPS group on the same postnatal day.