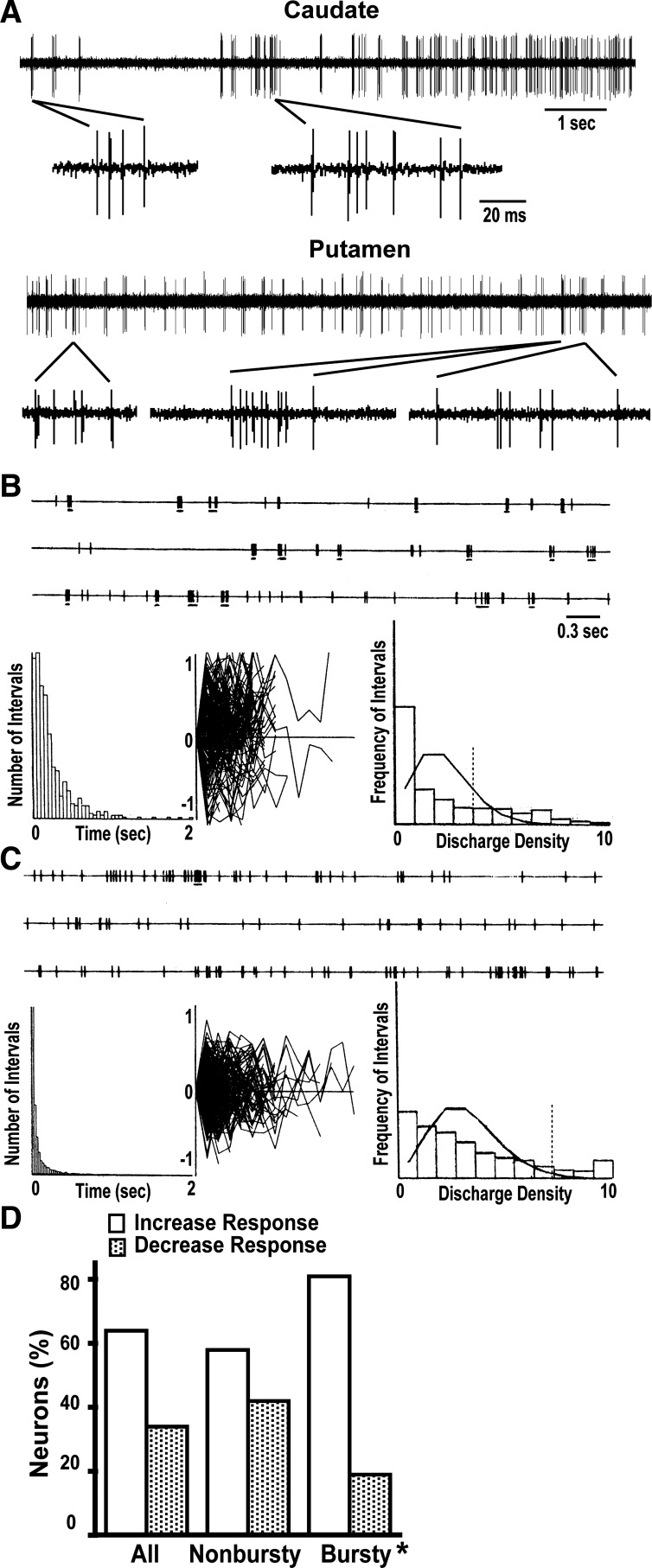
Fig. 2.
Examples of burst activity in medium spiny neurons (MSNs) recorded in the chronic parkinsonian state. A: selected spike trains of MSNs in the caudate and putamen exhibiting clear burst activity in the off state. Both traces display 10 s of raw data, and selected segments are presented in a decreased time scale to visualize the burst composition. B: example of the burst detection analysis showing the raster (top), where bursts are marked by underlining; interspike interval (ISI) histogram (bottom left); intraburst ISIs normalized by the first ISI and plotted in decimal log values (−1 to 1; bottom center); and discharge density histogram (DDH; bottom right) with the Poisson distribution curve (histogram shows the frequency of intervals t with a certain number of spikes starting from 0 at left and using a bin width of unity). The vertical dashed line in the DDH marks the threshold for burst detection. The analysis in this MSN (8.9-Hz firing frequency) shows a 1.1-Hz burst rate detected with t = 2/m (Poisson mean of 2) and a threshold bin of 4 for a significant deviation of the Poisson process (dashed line). Spike mean in a burst was 5.9 and mean ISI in bursts was 10.9 ms. The intraburst ISI plot does not show serial changes compatible with consistent increasing intervals as found in certain burst activity during sleep. C: example of another unit (37.1-Hz firing frequency) where a 1.82-Hz burst rate was detected using t = 3/m (Poisson mean of 3) and the threshold bin for a significant deviation of the Poisson process was 8 (dashed line). Spike mean in a burst was 5.4, and mean ISI in bursts was 5.5 ms. Notice the lack of evidence for burst activity in the ISI histogram compared with the DDH. Descriptions and conventions are the same as in B. D: distribution of the burst activity pattern in MSN subpopulations suggested by the change of firing frequencies in response to dopamine (increase or decrease of frequency is presumed to correspond to D1 or D2 receptor-mediated response, respectively). The bursty pattern of activity is predominantly exhibited in MSNs with dopamine-induced activity increases. *P < 0.001, observed vs. expected; χ2 test.