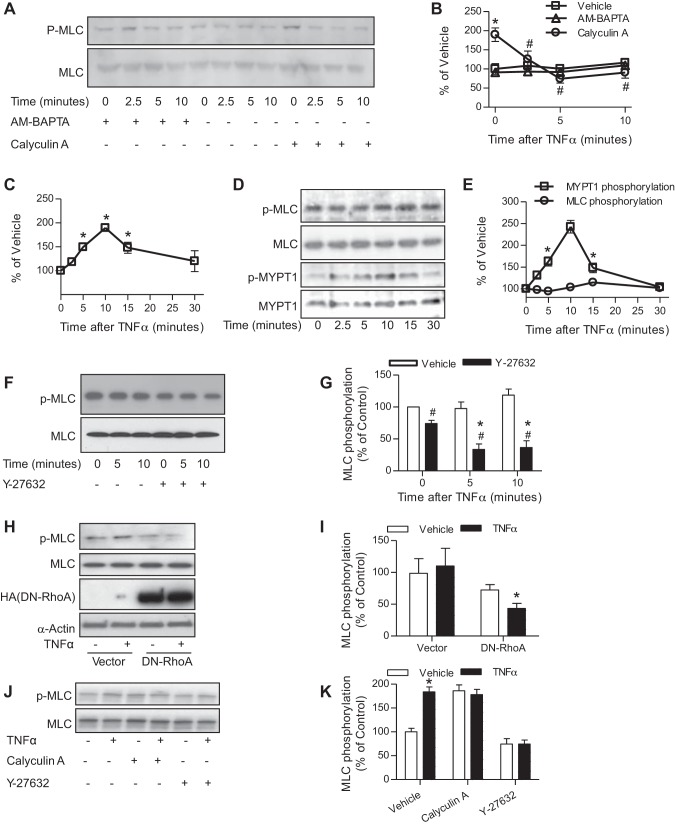
Fig. 3.
TNF-α activates RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway. A and B: HVSMCs were pretreated with AM-BAPTA (10 mM) or calyculin A (0.3 μM) for 15 min, followed by treatment with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for the indicated time and then subjected to MLC phosphorylation analysis by Western blot. The representative images (A) and summary (B) of 4 independent experiments are presented. *P < 0.05 vs. vehicle of the same time point; #P < 0.05 vs. calyculin A of 0 min, two-way ANOVA. C–E: HVSMCs were treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for the indicated time. GTP-bound RhoA (C; n = 4) was assessed by the RhoA G-LISA activation assay (cytoskeleton); MLC and MYPT1 phosphorylation (D and E; n = 3) was analyzed by Western blot. *P < 0.05 vs. 0, one-way ANOVA. F and G: HVSMCs were pretreated with vehicle or Y-27632 (10 μM) for 30 min and followed by treatment with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for the indicated time. MLC phosphorylation was then analyzed by Western blot; n = 3. *P < 0.05 vs. 0; #P < 0.05 vs. vehicle, two-way ANOVA. H and I: HVSMCs were transfected with vector or plasmid that expresses HA-tagged dominant negative RhoA (DN-RhoA) and treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 5 min. MLC phosphorylation was then analyzed by Western blot; n = 3. *P < 0.05 vs. vehicle, two-way ANOVA. J and K: vascular smooth muscle cells were isolated from SM22-CreIKK2flox/flox mice and treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 5 min in the presence of calyculin A (0.3 μM) or Y-27632 (10 μM); n = 3. *P < 0.05 vs. vehicle, two-way ANOVA.