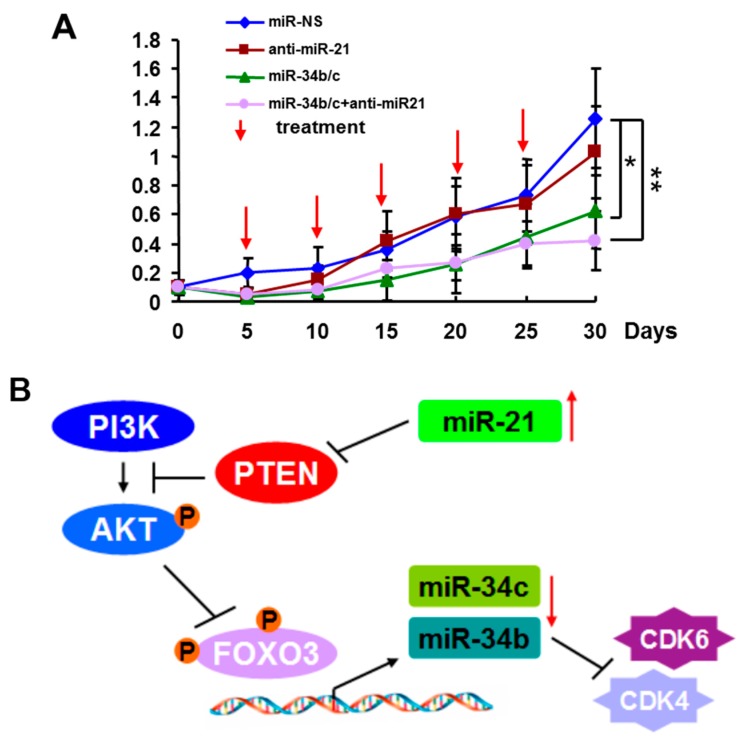
Figure 4.
Systematic delivery of miR-34b/c or with anti-miR-21 inhibited breast tumor growth. (A) MDA-MB-231 cells were subcutaneously injected into immunodeficient mice. Tumor volumes were measured every five days. At day five after tumor implantation, the mice were treated with formulated miR-Scr, anti-miR-21, miR-34b/c, or anti-miR-21 and miR-34b/c combination by intravenous (i.v.) tail vein every five days. Tumor volumes were measured every five days and presented. (mean ± SEM; n = 8). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; and (B) A model of the miR-21-FOXO3a-miR-34b/c signaling in breast cancer. Oncogenic miR-21 up-regulation promoted PI3K/AKT signaling activation through directly inhibiting PTEN expression, a suppressor of PI3K/AKT. The activation of AKT phosphorylates FOXO3a resulting in relocalization of FOXO3a proteins from nucleus to the cytoplasm. Nuclear FOXO3a down-regulation reduced the binding efficiency of FOXO3a in the promoter of miR-34b/c leading to decreases in the expression levels of miR-34b and miR-34c in cells.