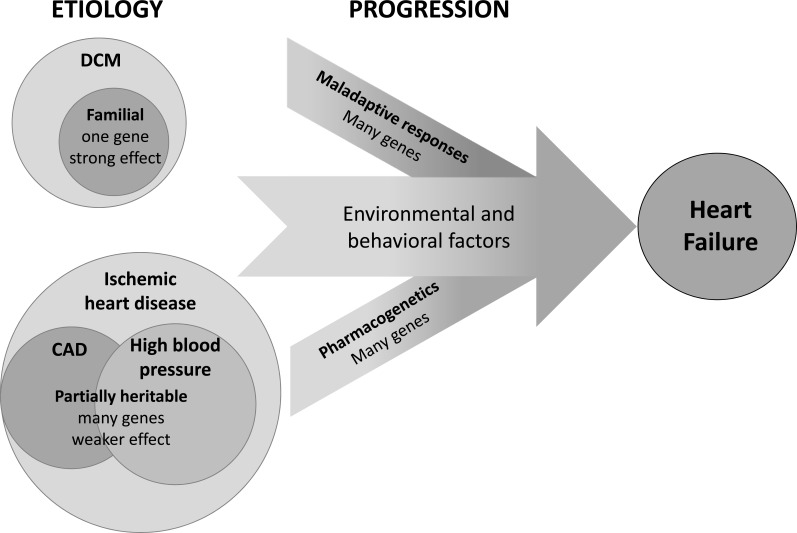
Fig. (1).
Heart failure arises from a complex interaction between genetic and environmental factors. Genetic factors may influence the susceptibility to the underlying etiology of heart failure, the progression of the disease, or the response to pharmacologic therapy. Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) can result directly from a mutation in a single gene, but the genetic component of heart failure typically consists of interacting variants in many genes with minor individual effects.