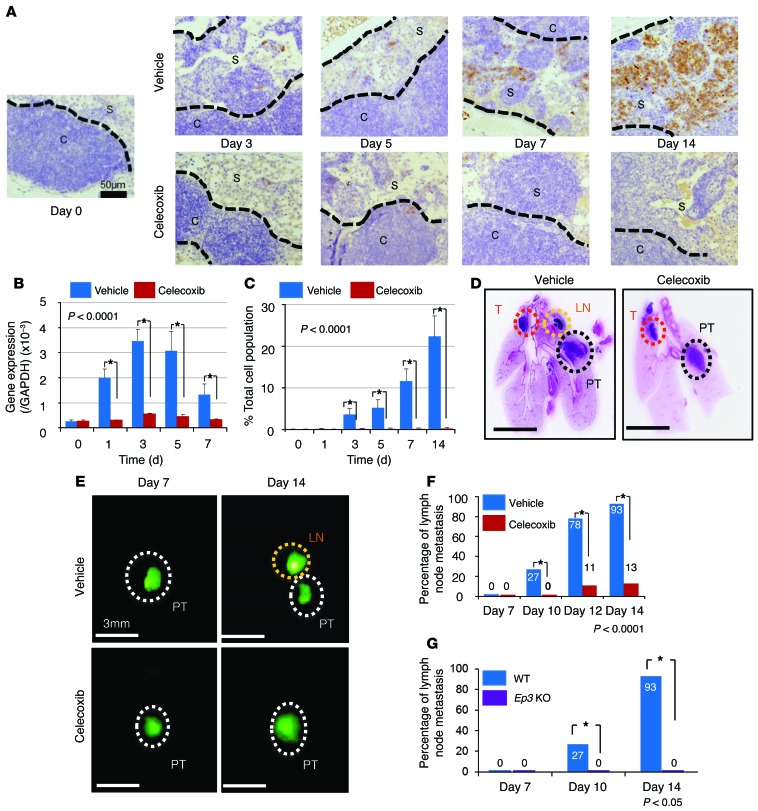
Figure 1. COX-2 induction in regional lymph nodes and the effect of COX-2 inhibition on regional LNM.
(A) Immunohistochemical COX-2 staining of the regional lymph nodes after lung LLC cell implantation. In vehicle-treated mice, COX-2–positive cells were localized in the subcapsular regions. Celecoxib was given orally throughout the experimental period. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) RT-PCR analysis of Cox2. Cox2 mRNA levels were significantly reduced in the celecoxib-treated group compared with the vehicle-treated group. n = 15 per group. *P < 0.0001 (ANOVA). (C) The percentage total cell population of COX-2–positive cells was significantly reduced in the celecoxib-treated group compared with the vehicle-treated group. n = 15 per group. *P < 0.0001 (ANOVA). (D) Loupe images by typical H&E staining obtained on day 10 after injection. Scale bars: 5 mm. (E) Fluorescence microscope images obtained after implantation of GFP-positive LLC cells into the lung. Scale bars: 3 mm. (F) Temporal changes in the percentage of regional LNM–positive mice. Metastasis in the vehicle-treated group was compared with that in the celecoxib-treated group. n = 15 per group. *P < 0.0001 (χ2 test). (G) Percentage of regional LNM–positive mice. Metastasis was compared between Ep3 KO mice and WT mice. WT, n = 15; Ep3 KO, n = 5. *P < 0.05 (χ2 test). Error bars indicate the mean ± SD. N indicates the number of mice tested. S, subcapsular regions; C, cortex; PT, primary tumor; LN, lymph node; T, thymus.