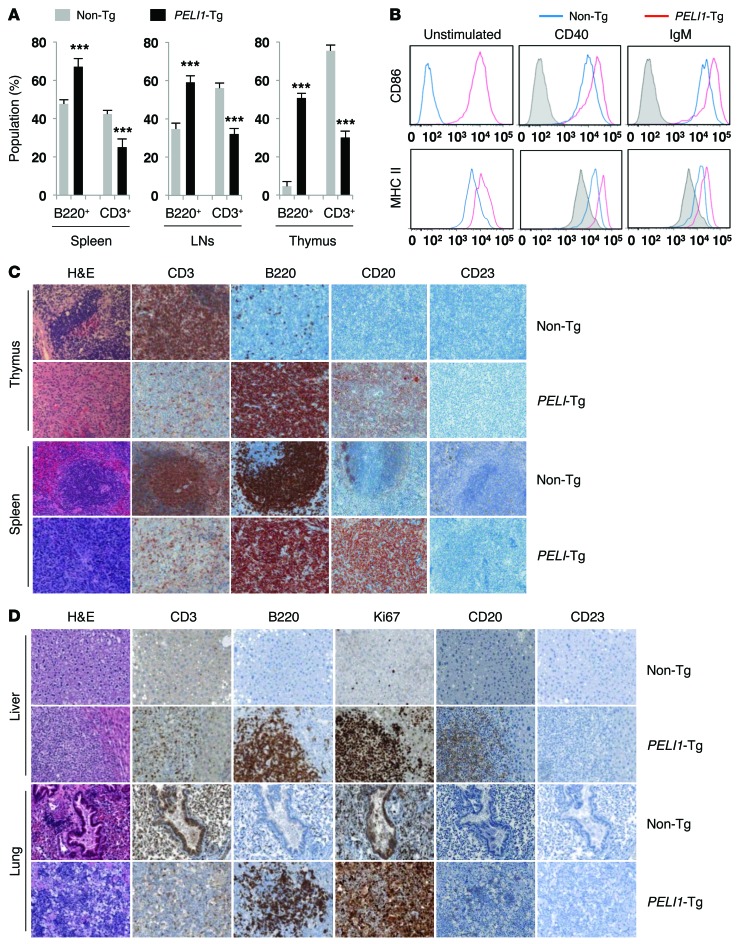
Figure 2. Constitutive PELI1 expression promotes hematopoietic alterations and activates ligand-independent B cell signal transduction.
(A) Proportion of B220+ B cell and CD3+ T cell populations, measured by flow cytometry, in cells isolated from spleen, LN, and thymus of non-Tg and PELI1-Tg mice at 14–16 months of age. Data (mean ± SEM) are representative of 3 independent experiments, with 4 mice per experiment. ***P < 0.001. (B) Flow cytometry of CD86 and MHC class II surface expression in splenic cells derived from non-Tg and PELI1-Tg mice incubated in vitro for 24 hours in the presence of anti-CD40 and anti-IgM antibodies. Gray histograms represent untreated non-Tg cells (unstimulated control). (C) Representative images of H&E staining and IHC analyses for B220, CD3, CD20, and CD23 antigen expression in splenic and thymic tissue samples isolated from non-Tg and PELI1-Tg mice. Strong B220 and CD20 staining was observed in the spleen and thymus of PELI1-Tg mice, whereas B220 and CD20 staining was detectable only at the GC of control non-Tg mice. Original magnification, ×200. (D) Liver and lung tissue samples isolated from non-Tg littermates and PELI1-Tg mice were fixed and stained with anti-B220, anti-CD3, anti-CD20, anti-CD23, and anti-Ki67 antibodies in serial sections. Original magnification, ×200.