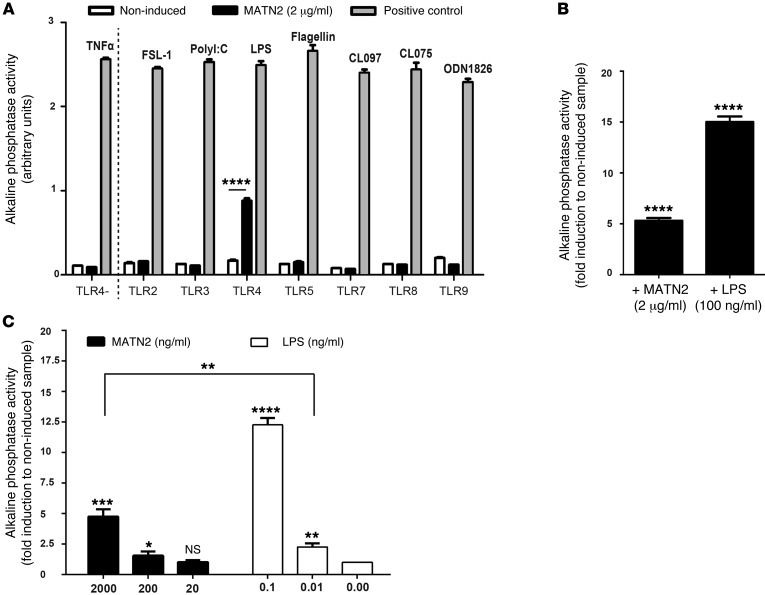
Figure 8. MATN2 signals through TLR 4.
(A) Screening for MATN2-triggered (2 μg/ml) activation of the alkaline phosphatase reporter via TLR/NF-κB signaling in genetically modified HEK293 cells expressing the indicated type of TLR (black bars). Alkaline phosphatase activity (arbitrary units) is used as an indicator for TLR stimulation. As positive control, cell lines were induced with a receptor-specific ligand. TLR2, heat-killed Listeria monocytogenes at 108 cells/ml; TLR3, poly(I:C) at 1 μg/ml; TLR4, E. coli K12 LPS at 100 ng/ml; TLR5, S. typhimurium flagellin at 100 ng/ml; TLR7, CL097 at 1 μg/ml; TLR8, CL075 at 10 μg/ml + poly(dT) 10 μM; and TLR9, CpG ODN 1826 at 100 ng/ml. Noninduced TLR clones were used as negative controls (white bars), and a HEK293 cell line expressing only alkaline phosphatase but not TLR4 was used as specific TLR4 negative control (TLR4–). (B and C) Fold induction in alkaline phosphatase triggered by (B) 2 μg/ml MATN2 or 100 ng/ml LPS or by (C) the indicated doses of MATN2 or LPS. Note that the response elicited by 2,000 ng/ml MATN2 is significantly greater than that of the trace LPS concentration of 0.01 ng/ml (P = 0.003). ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05.