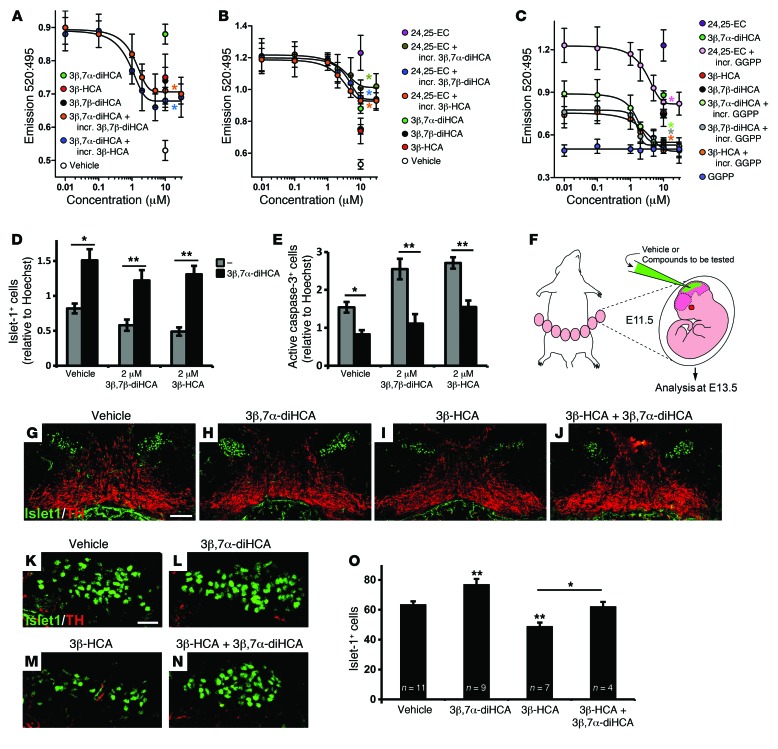
Figure 5. Competition between cholestenoic acid effects, and 3β,7α-diHCA promotes motor neuron survival in vivo.
(A–C) TR-FRET LXRβ coactivator assays. (A) The effect of 10 μM 3β,7α-diHCA was dose-dependently competed by increasing concentrations (incr.) of 3β,7β-diHCA and 3β-HCA (both *P < 0.05 for ≥2 μM). Similarly, (B) the effect of 10 μM 24,25-EC was dose-dependently competed by 3β,7α-diHCA (*P < 0.05 for ≥10 μM), 3β,7β-diHCA (*P < 0.05 for ≥10 μM), and 3β-HCA (*P < 0.05 for ≥5 μM), and (C) the effects of 3β,7α-diHCA, 3β-HCA, 3β,7β-diHCA, and 24,25-EC (all 10 μM) were dose-dependently competed by GGPP (all *P < 0.05 vs. respective no-GGPP group). Data were analyzed by Mann-Whitney test. (D and E) 10 μM 3β,7α-diHCA rescued the toxic effect of 2 μM 3β,7β-diHCA or 3β-HCA on islet-1+ cells and reduced neuronal cell death induced by these acids, as indicated by the number of active caspase-3+ cells, in mouse E11.5 brain primary cultures. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, Mann-Whitney test. (F) Mouse embryos were injected with vehicle or cholestenoic acid into the mesencephalic ventricle in utero at E11.5 and collected at E13.5. (G–N) Midbrain coronal sections showing islet-1+ motor neurons (green) and neighboring TH+ neurons (red) (G–J), and higher magnification of islet-1+ cells (K–N), for embryos injected with vehicle (G and K), 5 μM 3β,7α-diHCA (H and L), 1 μM 3β-HCA (I and M), and 1 μM 3β-HCA plus 5 μM 3β,7α-diHCA (J and N). (O) Quantification of islet-1+ cell number in each group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, 1-way ANOVA with LSD post-hoc test. Scale bars: 100 μm (G–J); 20 μm (K–N). All data are mean ± SEM (n = 3).