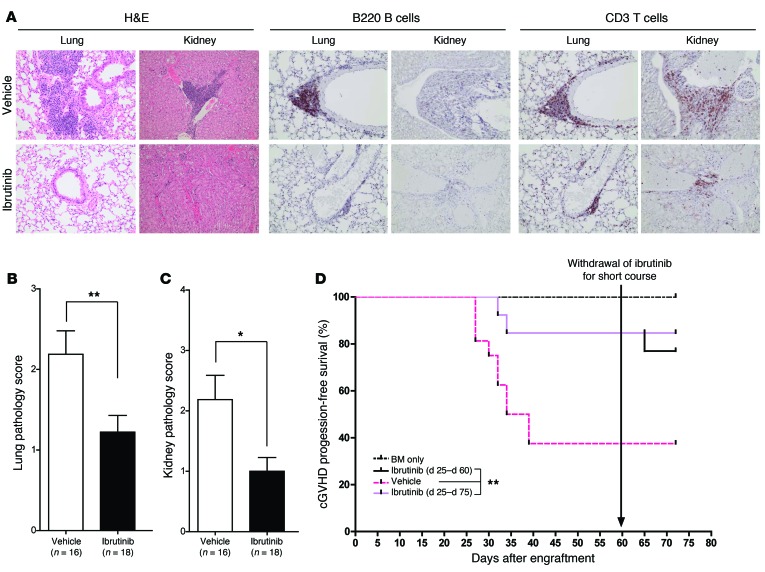
Figure 3. Ibrutinib therapy prevents autoimmune injury in a T cell–dependent model of cGVHD.
(A) Representative images from H&E-, B220-, or CD3-stained lung and kidney tissues from mice sacrificed at day 125 after HSCT from 6 mice/group. Images were taken by a trained veterinary pathologist who was blinded to animal cohorts. Original magnification, ×200. (B) Blinded pathologic analysis of H&E-stained lung tissues obtained from cGVHD cohorts (18 vehicle and 18 ibrutinib). Lymphohistiocytic infiltration was graded on a 0 to 4 scale for each animal. (C) Blinded pathologic analysis of H&E-stained kidney tissues obtained from cGVHD cohorts. Portal hepatitis and vasculitis were graded on a 0 to 4 scale for each animal. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (D) Kaplan-Meier plot of cGVHD progression-free survival in an independent experiment aimed to determine sustained benefits from continued ibrutinib therapy. During the course of the experiment, ibrutinib was withdrawn on day 60 from animals in the Ibrutinib (day 25 to day 60) cohort. **P < 0.001.