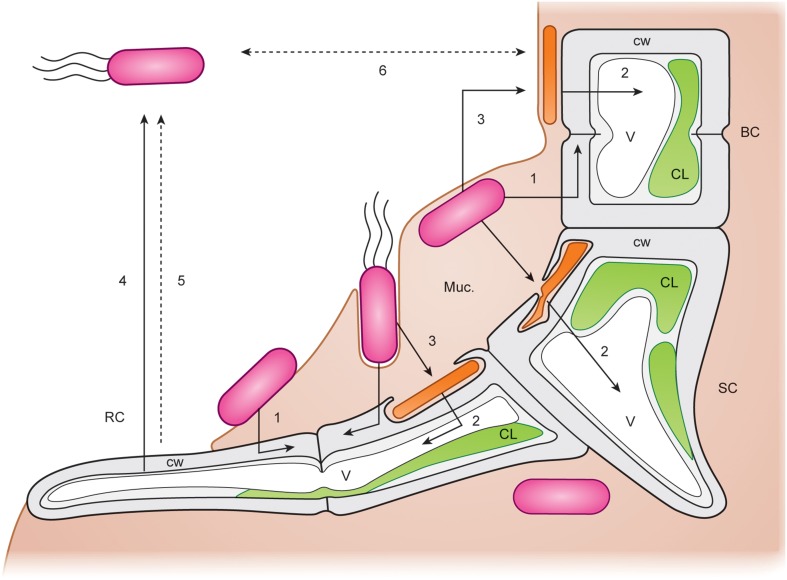
Figure 8.
Potential cross-kingdom interactions. Detailed working model for the interactions of Ulva mutabilis with Cytophaga sp. (MS6) (orange rods) and Roseobacter sp. (MS2) (pink rods with or without flagellae). Arrows indicate possible chemical interactions. BC, blade cell; SC, stem cell; RC, rhizoid cell of U. mutabilis (wildtype) germling. CW, algal cell wall; V, vacuole; C, chloroplast; Muc, mucilage in which the bacteria are embedded. (1) Roseobacter stimulates Ulva cell divisions and (2) Cytophaga induces Ulva cell growth stimulating vacuole extension by released morphogenetic regulators and promotes rhizoid and correct cell wall formation. (3) Roseobacter may promote Cytophaga viability. (4) Rhizoid cells of U. mutabilis produce a factor attracting Roseobacter by chemotaxis. (5) Antibiotic substances produced by the alga control growth of inappropriate bacteria and other epiphytes (Hornsey and Hide, 1985). (6) Quorum-sensing system of Roseobacter and Cytophaga mutually regulates the appropriate bacterial cell densities (adapted, colored and used with permission from Spoerner et al., 2012; Copyright© 2012, Wiley).