Figure 5. Alteration of asparagine 394 abolishes LytS phosphatase activity.
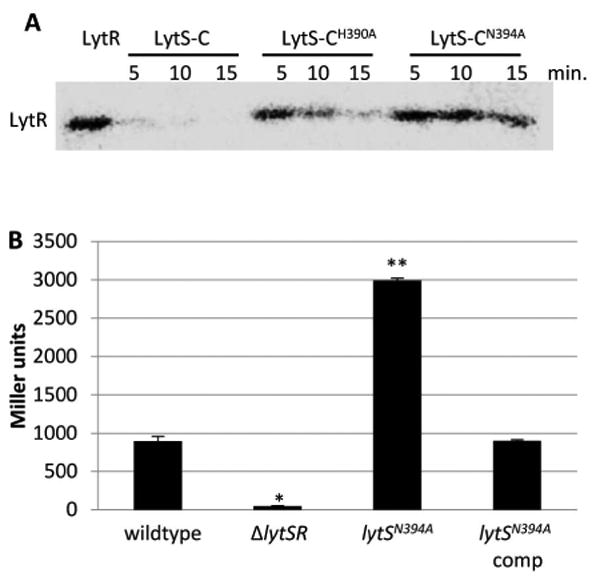
A. Phosphatase assays. Purified LytR-N was radiolabeled with [γ32P]AcP and mixed with equal molar amounts of LytS-C, LytS-CH390A, or LytS-CN394A. Samples were taken every 5 minutes, separated in a 15% SDS-PAGE gel and radiolabeled proteins visualized using a phosphor imager. Phosphatase activity is manifested as a reduction of LytR phosphorylation. B. β-galactosidase assays. Cultures of KB5019 (wildtype), KB5020 (ΔlytSR), KB5032 (lytSN394A), KB5032 (pML11) (lytS complement) were grown in TSB to late exponential phase, harvested, and the β-galactosidase activity (Miller Units) generated by the chromosomal PlrgAB-lacZ was measured. The data presented are the average of two biological replicates (n=2) with standard error of the mean indicated. A two-tailed Student T-test assuming equal variances was used to determine statistical significance compared to wildtype. *p<0.05, **p<0.005
