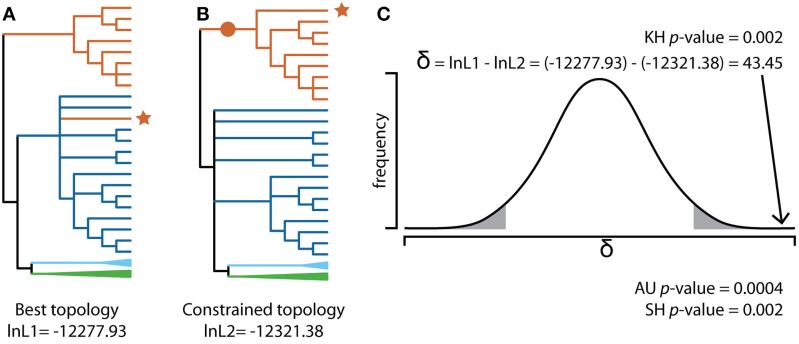
Figure 3.
Evaluating HGT using a comparative topology test. (A) Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogeny of homologous sequences to stcI, a gene in the sterigmatocystin SM cluster, in Podospora anserina identified from a BLAST search of 161 Pezizomycotina genomes (JGI Mycocosm, download date 5 July 2014). Sequences were aligned and trimmed using MAFFT (Katoh and Standley, 2013) and trimAL (Capella-Gutierrez et al., 2009), respectively, and the phylogeny was created using RAxML (Stamatakis, 2014) using the PROTGAMMAAUTOF amino acid model of substitution and 100 bootstrap replicates. The resulting cladogram was midpoint rooted and branches supported by less than fifty bootstrap replicates were collapsed. This ML best tree depicts Podospora anserina (Sordariomycetes; red branch with red *) grouping with Eurotiomycetes (dark blue branches). Other taxa in the phylogeny include additional Sordariomycetes (red branches), Leotiomycetes (light blue collapsed clade) and Dothideomycetes (green collapsed clade). (B) Best ML phylogeny using the same input data, but with the constraint imposed that Podospora anserina must group with other Sordariomycetes (red •). All other branches were resolved to obtain the maximum log-likelihood (-lnL), given the alignment using RAxML. (C) The difference in likelihood scores was evaluated to determine if the best topology represents a significantly better explanation of the data compared to the constraint topology. The Kishino–Hasegawa (KH) test (Kishino and Hasegawa, 1989) assumes a normal distribution of log-likelihood differences (δ). In this example, δ = 43.45 lies within the rejection region (gray area under curve) so one can reject the null hypothesis that the best topology is not statistically significantly better than the constraint topology (KH p-value = 0.002). Other tests, such as the Shimodaira–Hasegawa (SH) test (Shimodaira and Hasegawa, 1999) and the Approximately Unbiased (AU) test (Shimodaira, 2002), improved upon the KH test by correcting for multiple comparisons as well as the fact that the ML best tree is known a priori. In this example, both the SH test and AU test also reject the null hypothesis. All comparative topology tests were run in CONSEL (Shimodaira and Hasegawa, 2001).