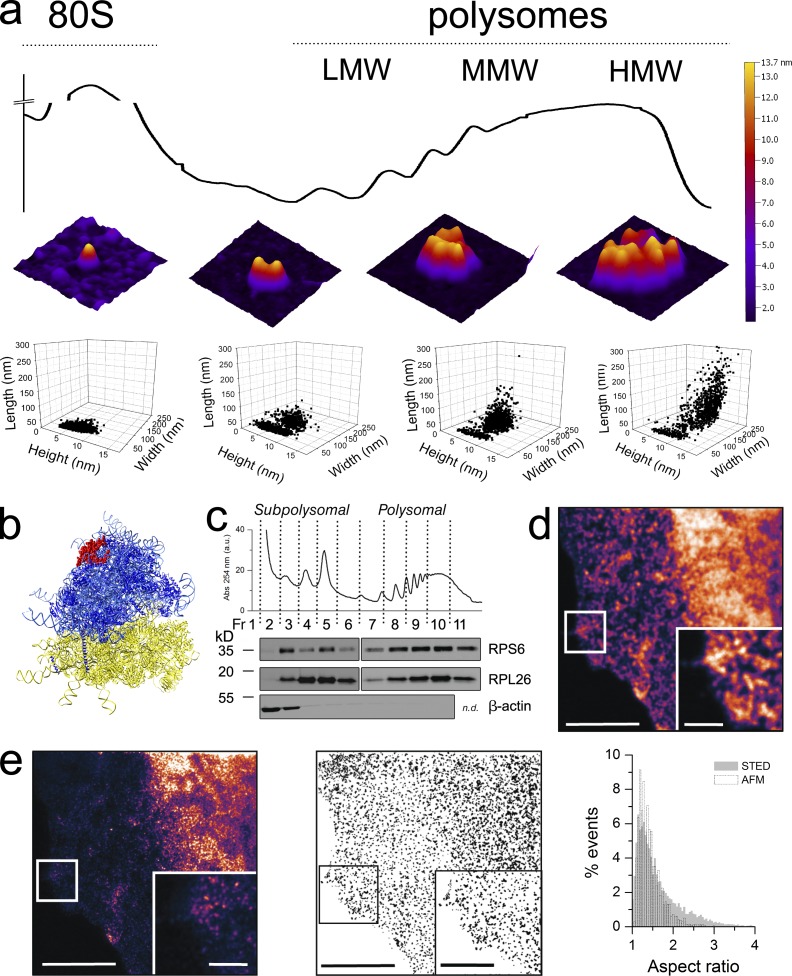
Figure 1.
Native human polysomes observed by AFM preserve their in vivo organization and reveal tight ribosome interactions. (a) Typical sedimentation profile of polysomes from MCF-7 cell lysates obtained in a concave 15–50% sucrose gradient. The absorbance peaks corresponding to 40S and ribonucleoparticles are not shown for clarity. Fractions containing 80S, LMW, MMW, and HMW polysomes observed by AFM in air are shown as 3D projections (middle row). In the bottom row, the grain analysis of AFM structures is reported, showing the height, width, and length scatterplot for the 80S, LMW, MMW, and HMW polysomes. The 80S fraction data look to be grouped in a single cluster, which is also present in the other three fractions, alongside a second cluster that displays an increase of width and length along the gradient. The total number of objects considered are 1,319 (80S), 1,319 (LMW), 925 (MMW), and 1,187 (HMW) obtained from one to three independent polysomal profiles. (b) Side view of the crystal structure of the human ribosome (Anger et al., 2013) showing the position of RPL26 (or RPL24 according with the new nomenclature proposed by Jenner et al., 2012; in red) at the top of the 60S subunit. (c) RPS6 and RPL26, core proteins of the small and large ribosomal subunit, respectively, are present along sucrose fractions as revealed by Western blotting analysis. Actin is used as a control for nonribosomal fractions and does not cosediment with ribosomes, ribosomal subunits, and polysomes. (d) Magnification of MCF7 cytoplasm immunolabeled with ATTO-488 against RPL26 and imaged by confocal microscopy. (e, left) The same image as in d imaged with g-STED and magnification of cytoplasmic granules. The subdiffraction x–y resolution at 488 nm is <45 nm. The image shown is from a single representative experiment out of three repeats. For the further analysis, we used nine images. (middle) Example of MCF7 image processing for particle analysis and extraction of shape parameters after binarizing and thresholding (see Materials and methods for details). (right) AFM and STED shapes of polysomes are compared plotting the normalized distributions of the aspect ratio (ratio of the major axis to the minor axis) of each particle (3,219 and 8,757 objects, respectively). Bars: (d and e) 5 µm; (d, inset) 1 µm; (e, inset) 2 µm.