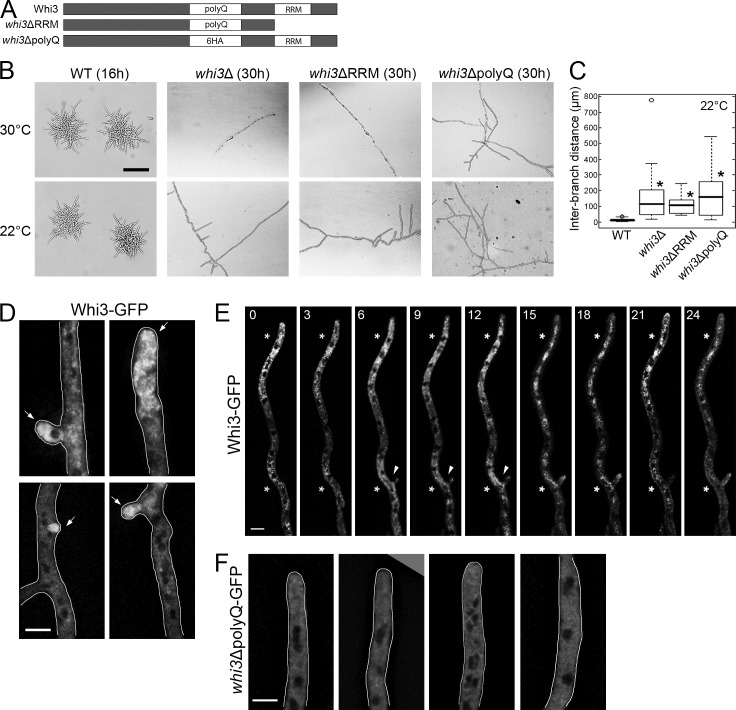
Figure 1.
The polyQ tract and RRM domain of Whi3 are required for symmetry breaking. (A) Diagrams of wild-type and mutant Whi3 constructs. Six HA repeats replace the polyQ tract (the same size) for whi3ΔpolyQ. (B) Wild type and whi3 mutants grown at 30 or 22°C. Bar, 200 µm. (C) Distances between neighboring lateral branches on the hypha were measured for each strain (n > 50). *, P < 0.01 compared with wild type using a KS test. For all box-and-whiskers plots in this paper, the top and bottom of box indicate the 75th and 25th quartile, respectively. The thick line in the box shows the median, whiskers indicate maximum and minimum data points, and open circles indicate outliers. (D–F) Whi3 or Whi3ΔpolyQ proteins are localized in the hypha. Arrow, polarization site. Cells are outlined in gray. Bars, 5 µm. (D and F) Images are z-projected (>8 planes). (E) Montage of time-lapse movie. Time points (min) are indicated at the top of the images. Asterisks indicate concentrated Whi3. Arrowheads indicate emergence of a new branch. A single focal plane is shown.