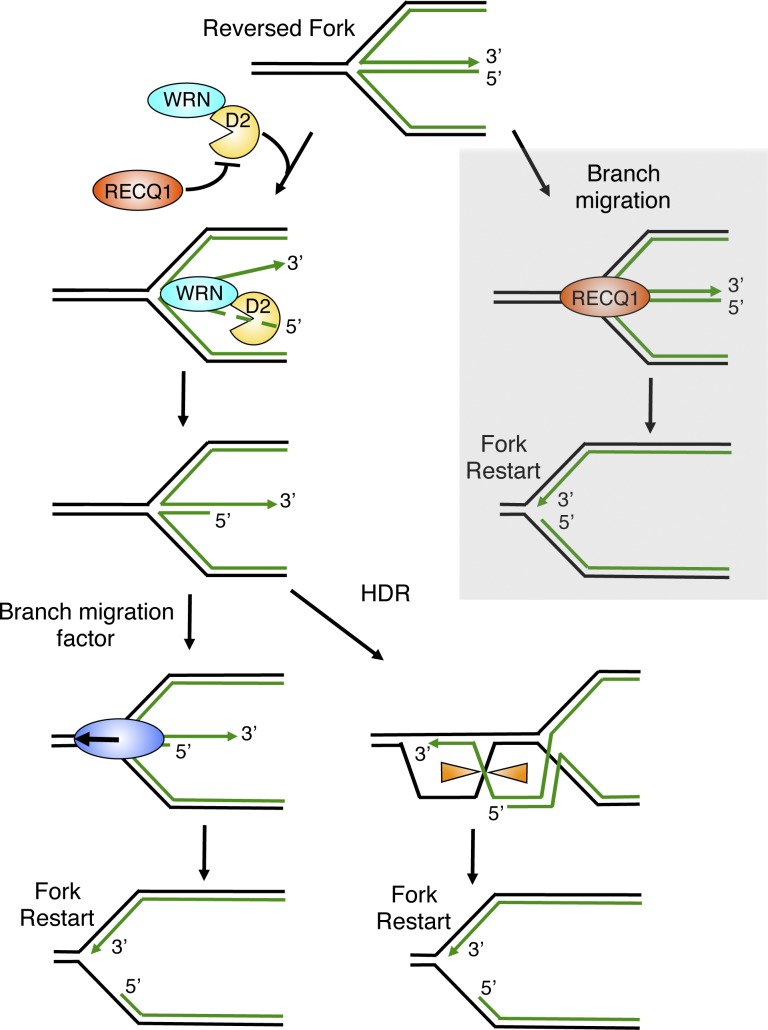
Figure 9.
Schematic model for the combined roles of DNA2 and WRN in reversed fork processing. DNA2 and WRN functionally interact to process reversed forks. DNA2 degrades reversed forks with a 5′-to-3′ polarity. WRN ATPase activity assists DNA2 degradation possibly by promoting the opening of the reversed arm of the fork. RECQ1 limits DNA2 activity by an ATPase-independent function. Branch migration factors specifically recognize the partially resected reversed forks to promote fork restart. Alternatively, the newly formed 3′ overhang of the reversed fork invades the duplex ahead of the fork, resulting in Holliday junction structures that can be resolved by specific resolvases or dissolvases to promote fork restart. Gray box, RECQ1 can independently restart reversed forks by virtue of its ATPase and branch migration activity.