Fig. 4.
TgEFG localizes to the apicoplast via a non-canonical targeting signal
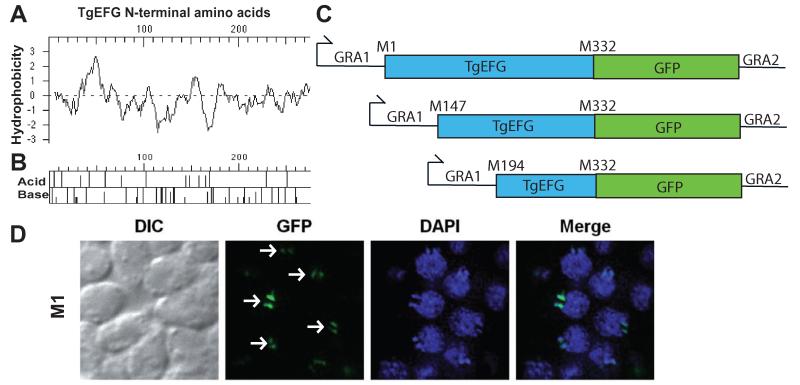
A. Kyte-Doolittle hydropathy plot of the first 275 amino acids of TgEFG. Positive numbers on the hydrophobicity axis indicate hydrophobic amino acids.
B. Acid/Base graph of the first 275 amino acids of TgEFG.
C. Diagrams of the TgEFG-GFP fusion constructs used to identify the start codon of TgEFG. The fusions started with M1, M147 or M194 of TgEFG, continued until M322 of TgEFG (blue box) and contained the entire GFP coding region (green box). The GRA1 promoter and 5′UTR was used on the 5′end of all constructs while the GRA2 3′UTR was used on the 3′end.
D. Only T. gondii expressing the TgEFG-GFP fusion where TgEFG began at the first in frame methionine showed localization to the apicoplast. The IFA used an anti-GFP antibody to visualize the TgEFG-GFP fusion (green) and DAPI to visualize nucleic acid (blue). White arrows indicate TgEFG-GFP in the apicoplast. Two spots are seen for each apicoplast because the apicoplasts have divided.