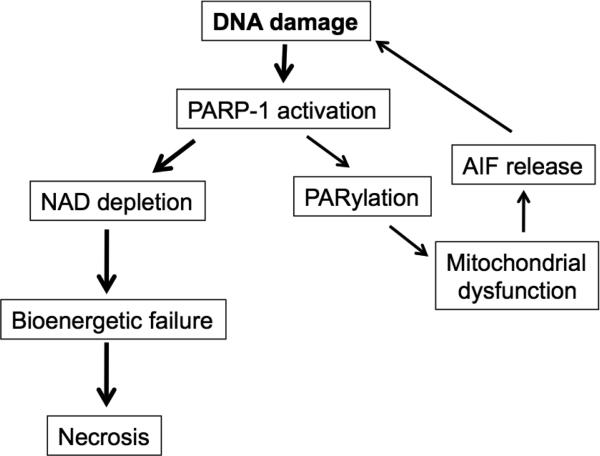
Figure 2. Molecular mechanisms of PARP-1 induced necrosis.
Extensive DNA damage caused by radiation or during inflammation activates PARP-1, a DNA sentinel. PARP1 uses its enzymatic substrate NAD to generate Poly-(ADP-Ribose) polymers (PARs) through a process termed PARylation. PARylation transmits signals from the nucleus to the mitochondra, which in turn release apoptosis inducing factor (AIF). AIF tranlocates to the nucleus and induces more DNA damage, which further activates PARP-1. Depletion of NAD as a result of extensive PARP-1 activation leads to bioenergetic collapse and necrosis.