Figure 1. AKAP12 is highly expressed in arachnoid cells that exhibit epithelial properties in the meninges.
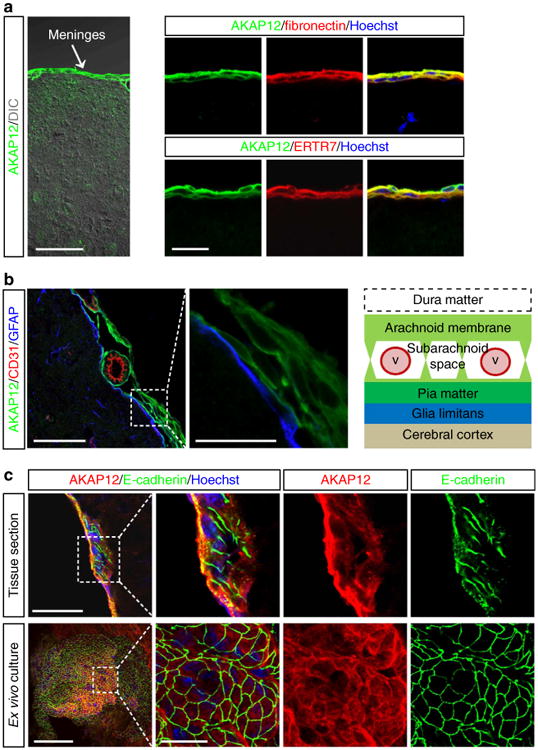
(a) AKAP12-positive cells are meningeal cells. Mouse brain sections were co-stained with antibodies against AKAP12 and meningeal cell markers (ERTR7 and fibronectin). Scale bar, 50 μm (left panel), 20 μm (right panels). (b) AKAP12-positive meningeal cells are meningeal arachnoid cells. Normal mouse brain sections were triple stained with antibodies against AKAP12, CD31 (a marker for endothelial cells) and GFAP (a marker for astrocytes). Scale bar, 50 μm (left panel), 20 μm (right panel). (c) AKAP12-positive meningeal cells highly express E-cadherin (a marker for arachnoid cells, a type of epithelial cell) in the normal meninges and in ex vivo-cultured meningeal tissue. Scale bar, 50 μm (upper panel), 100 μm (lower panel), 20 μm (magnified panels). Each panel represents the results from independent experiments repeated at least five times using different animals or conditions.
