Figure 1.
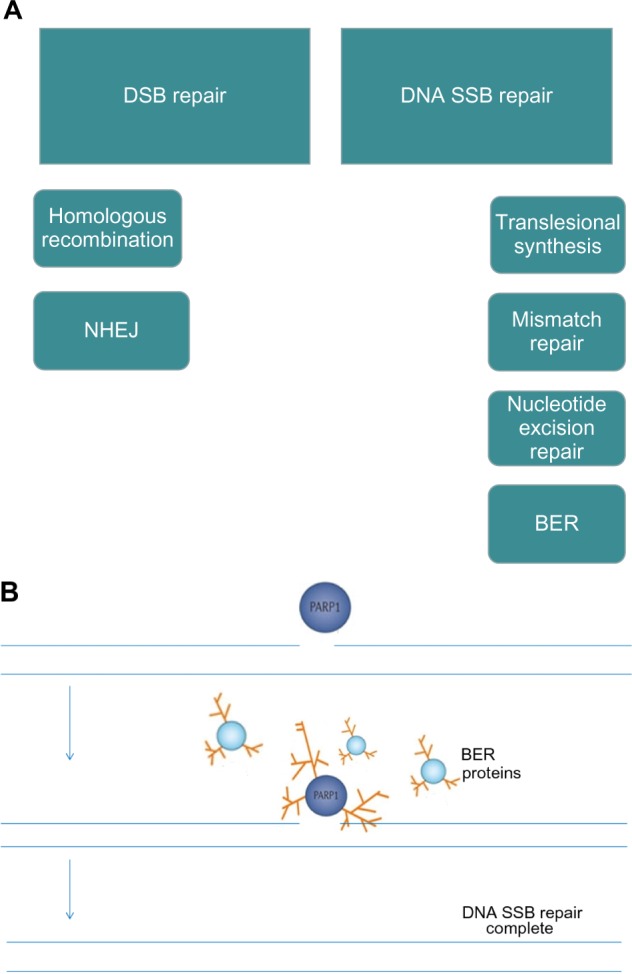
(A) DNA repair pathways; (B) PARP senses DNA SSBs and utilizes NAD+ as a substrate to form PAR, which attach to a range of target proteins including PARP-1 itself and BER proteins. This posttranslational modification is termed PARylation.
Notes: (A) There are six DNA repair pathways, two for repair of DNA DSBs and four for repair of SSBs. PARP is known to be involved in BER and has been shown to be a negative regulator of NHEJ (low-fidelity, error-prone pathway). PARP inhibition therefore leads to disruption of BER and in HR-deficient cells, increased reliance on error-prone NHEJ.53
Abbreviations: BER, base excision repair; DSBs, double-strand DNA breaks; HR, homologous recombination; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NHEJ, nonhomologous end joining; PAR, polymers of ADP-ribose; PARP, poly (adenosine diphosphate [ADP]) ribose polymerase; SSBs, single-strand DNA breaks.
