Figure 3. Effects of acute ethanol on ERK1/2 phosphorylation in the amygdala as a function of time.
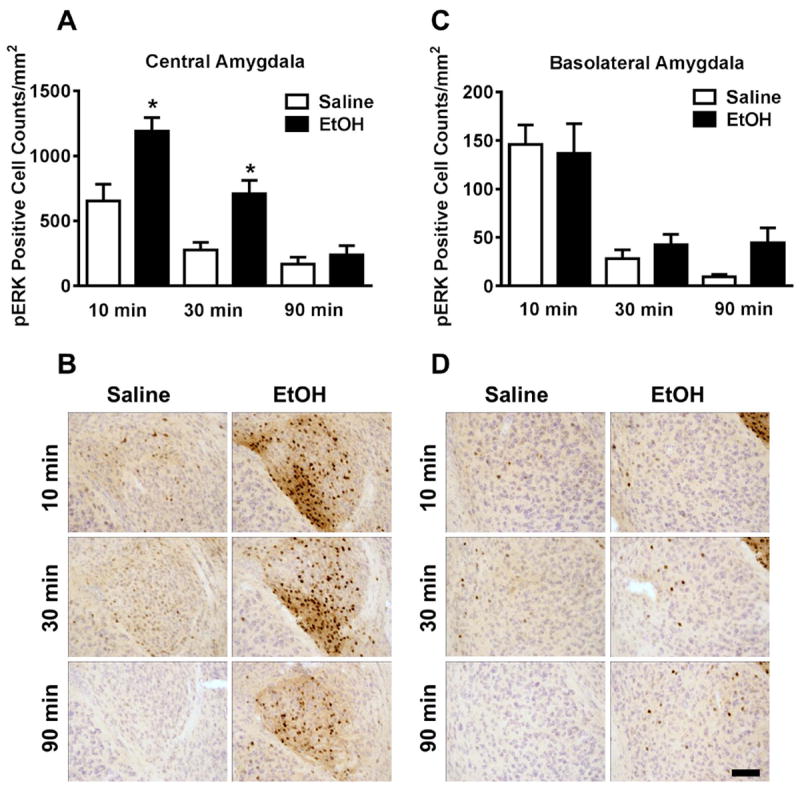
(A) Mean (± SEM) immunoreactivity of the pERK1/2 positive area in the central amygdala following 3.0 g/kg ethanol treatment expressed as relative change versus saline control. (B) Representative photomicrographs of the cytological pattern of pERK1/2 immunoreactivity in the central amygdala. (C) Mean (± SEM) immunoreactivity of the pERK1/2 positive area in the basolateral amygdala following 3.0 g/kg ethanol treatment expressed as relative change versus saline control. (D) Representative photomicrographs of the cytological pattern of pERK1/2 immunoreactivity in the basolateral amygdala (scale bar, 50 microns). *Significantly different from saline control at the given time point (p<0.05; Student’s t-test).
