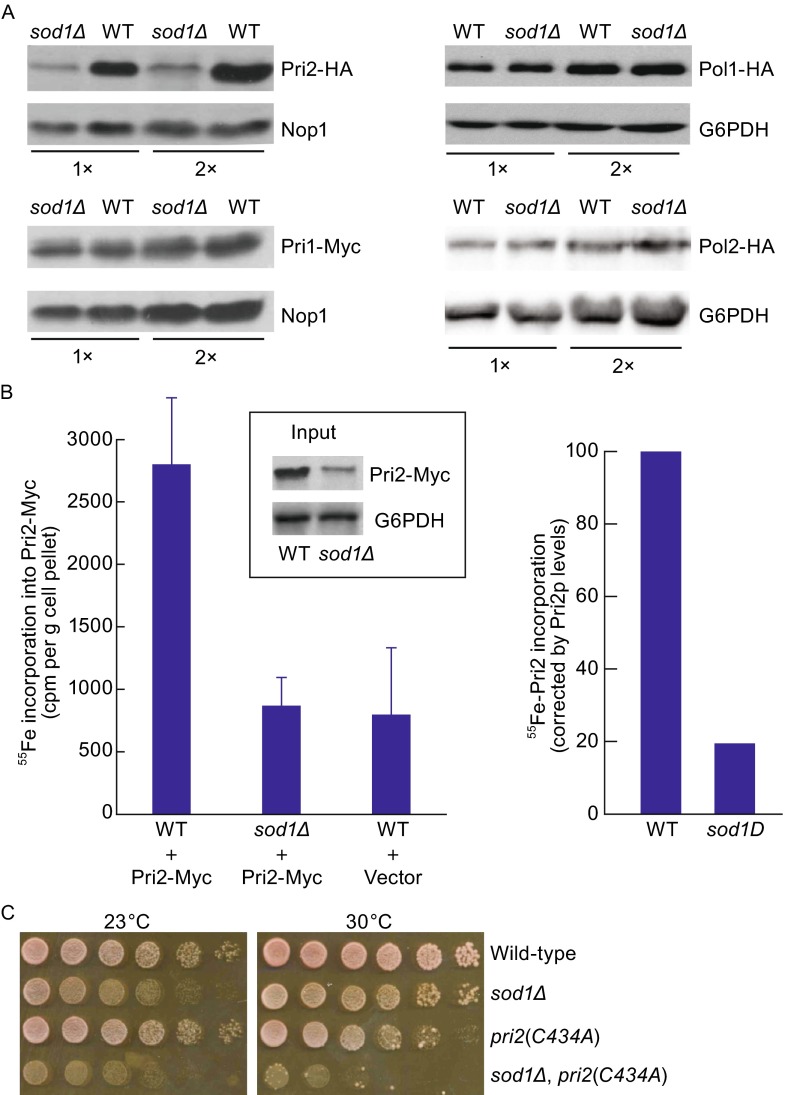
Figure 7.
Impaired Pri2 protein stability and iron binding in sod1Δ mutant cells. (A) Comparison of protein levels of Pri2, Pri1 and Pol1 between log-phase congenic wild-type and sod1∆ mutant cells. Pri2-HA, Pri1-Myc, Pol1-HA and Pol2-HA were expressed from their respective chromosomal loci under the endogenous promoters. Protein extracts were subjected to immunoblotting using monoclonal anti-HA and anti-Myc antibodies. Nop1 and G6PDH were probed as loading controls. (B) Fe-S cluster assembly on Pri2 protein is compromised in sod1∆ mutant. Congenic wild-type and sod1∆ cells harboring pRS426-PTDH3-Myc-Pri2 were grown and treated as described in the legend of Fig. 5B except for that radiolabeling with 55Fe was conducted for 2 h. The amount of 55Fe bound to immunoprecipitated Pri2 was quantified by scintillation counting (left panel) and corrected for the differences in Pri2 protein levels between wild-type and sod1∆ cells (right panel), as determined by immunoblotting and quantitative densitometry (insert). (C) Synthetic lethality between sod1∆ and pri2(C434A) mutant alleles. Congenic wild-type (LLY263), pri2(C434A) (LLY260), sod1∆ (LLY338) and pri2(C434A), sod1∆ (LLY427) mutant cells were harvested from log phase cultures and dot-plated on YPD medium in 10-fold serial dilutions starting at 105 cells. The plates were incubated at 23°C and 30°C for 2 days before being photographed