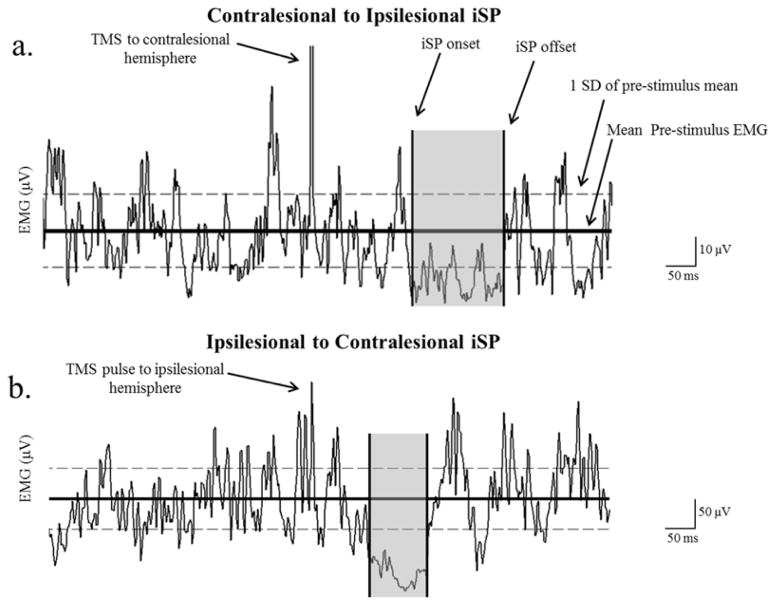
Figure 1.
Example of an ipsilateral silent period (iSP) from (a) contralesional to ipsilesional and (b) ipsilesional to contralesional hemisphere. The ISP ratio was the % EMG decrease of contralesional to ipsilesional/% EMG decrease of ipsilesional to contralesional hemisphere. ISP onset and offset were determined as the point where the EMG went below 1SD of the pre-stimulus mean and returned back within 1 SD of the pre-stimulus mean. Even though the patients maintained a contraction at 50% of the maximum voluntary contraction, it is important to notice the difference between the EMG scale of the paretic hand (a) and the non-paretic hand (b), where the paretic hand EMG reached a maximum of ~ 50 μV, and the non-paretic hand reached a maximum of ~ 400 μV. Despite the difference in EMG activity it has recently been shown that level of EMG does not influence the degree of inhibition.51 Results are reported as ISP ratio, which is defined as the Contralesional to Ipsilesional iSP/Ipsilesional to Contralesional iSP. The subject shown had an iSP ratio of .75.