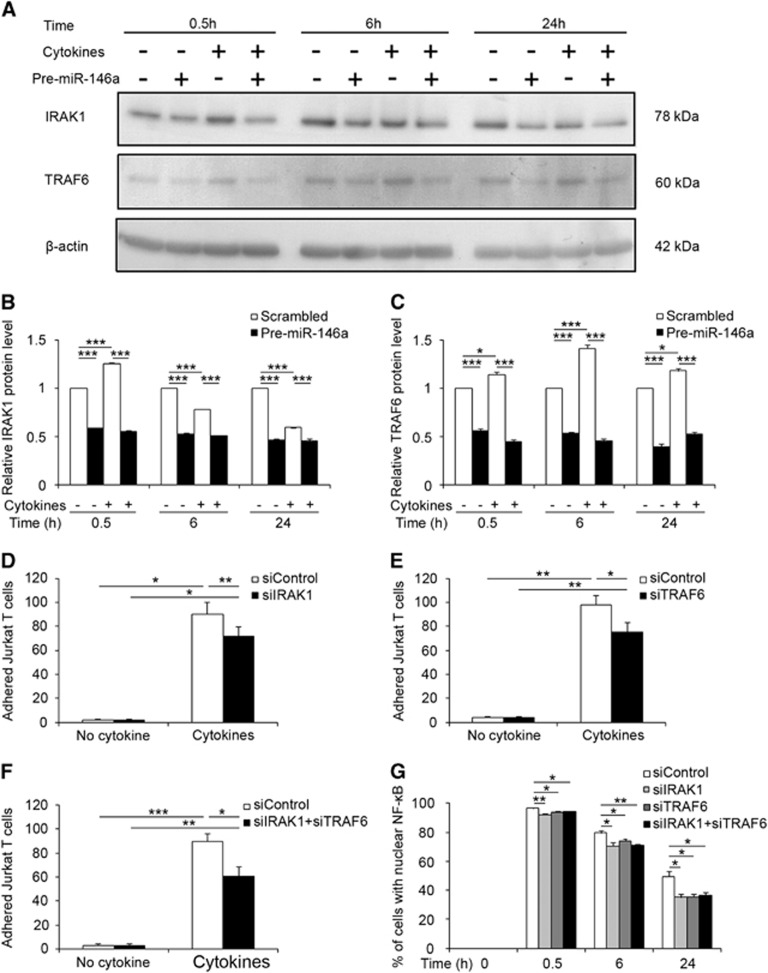
Figure 4.
miR-146a targets IRAK1 and TRAF6 to modulate NF-κB activation and Jurkat T-cell adhesion. (A) Western blot analysis show that overexpression of miR-146a via transfection with Pre-miR-146a repressed the expression of IRAK1 and TRAF6 in hCMEC/D3 cells either unstimulated or cytokine (1 ng/mL TNFα/IFNγ)-stimulated for 0.5, 6, and 24 hours. (B, C) Quantification of protein levels of IRAK1 and TRAF6 via ImageJ. Data represent mean±s.e.m., n=3, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 via analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post hoc comparison and Bonferroni correction. (D) Knockdown of the expression of IRAK1 via small interference RNA for IRAK1 (siIRAK1) decreased Jurkat T-cell adhesion to cytokine-stimulated hCMEC/D3 cells. (E) Knockdown of the expression of TRAF6 via siTRAF6 downregulated Jurkat T-cell adhesion to cytokine-stimulated hCMEC/D3 cells. (F) Knockdown of the expression of IRAK1 and TRAF6 simultaneously decreased Jurkat T-cell adhesion to cytokine-stimulated hCMEC/D3 cells. Data represent mean±s.e.m., n=3 to 4, *P<0.05, **P<0.05, ***P<0.001 via ANOVA. (G) Statistical analysis of the effects of siIRAK1 and siTRAF6 on nuclear translocation of NF-κB. Two-way ANOVA tests of all the time points after cytokine treatment demonstrate significant difference between the siControl and siIRAK1 or siTRAF6 or siIRAK1+siTRAF6 groups (P<0.01). One-way ANOVA was used to compare the difference with siControl at each time point. Data represent mean±s.e.m., n=3, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. IFNγ, interferon gamma; IRAK1, IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1; miR, microRNA; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha; TRAF6, TNF receptor-associated factor 6.