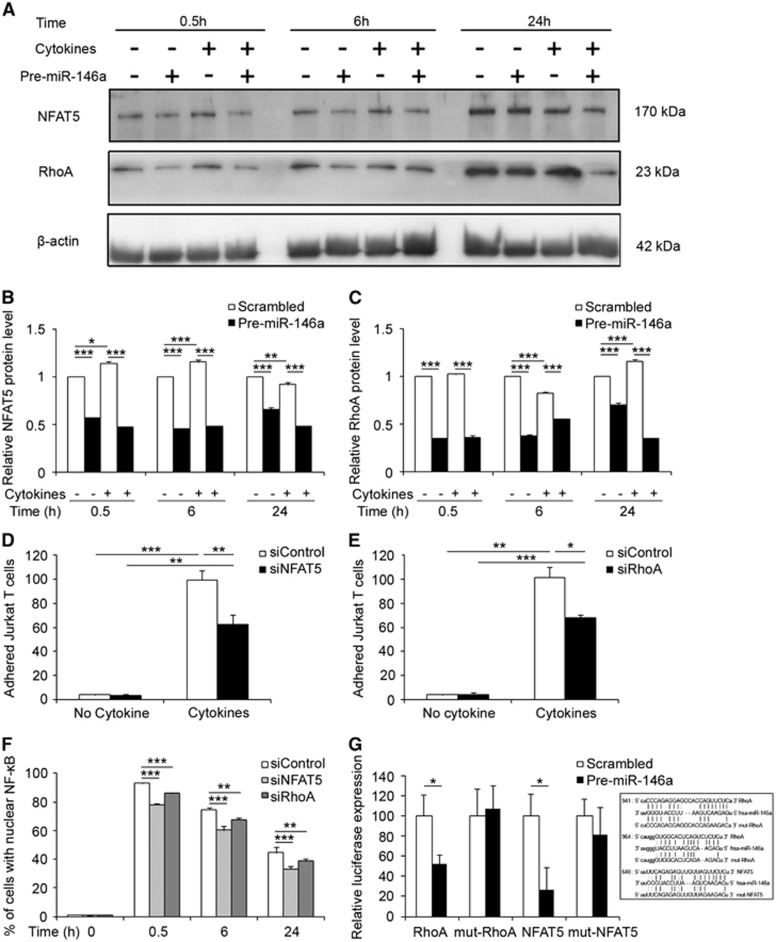
Figure 5.
miR-146a targets NFAT5 and RhoA to modulate NF-κB activation and Jurkat T-cell adhesion. (A) Western blot analysis show that overexpression of miR-146a via transfection with Pre-miR-146a repressed the expression of NFAT5 and RhoA in hCMEC/D3 cells either untreated or treated with cytokines for 0.5, 6, and 24 hours. (B, C) Quantification of protein levels of NFAT5 and RhoA via ImageJ. Data represent mean±s.e.m., n=3, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 via analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post hoc comparison and Bonferroni correction. (D) siNFAT5 decreased Jurkat T-cell adhesion to cytokine-stimulated hCMEC/D3 cells. (E) siRhoA downregulated Jurkat T-cell adhesion to cytokine-stimulated hCMEC/D3 cells. Data represent mean±s.e.m., n=3 to 4, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 via Student's paired t-test. (F) Statistical analysis of the effects of siNFAT5 and siRhoA on nuclear translocation of NF-κB. Two-way ANOVA tests of all the time points after cytokine treatment demonstrate significant difference between the siControl and siNFAT5 or siRhoA groups (P<0.001). One-way ANOVA was used to compare the difference with siControl at each time point. Data represent mean±s.e.m., n=3, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. (G) 3'-UTR luciferase assay demonstrated that miR-146a overexpression led to decreased luciferase activity in hCMEC/D3 cells transduced with lentiviral luciferase vector containing the 3'-UTR of RhoA or NFAT5 but not with the corresponding mutated 3'-UTR versions. Text box demonstrates a sequence alignment of human miR-146a (hsa-miR-146a) and two target sites in the 3'-UTR of RhoA and one target site in the 3'-UTR of NFAT5. Mutated 3'-UTR for RhoA or NFAT5 (mut-RhoA, mut-NFAT5) was performed by replacing the corresponding miR-146a target sites with four nucleotides: AAGA. Data represent mean±s.e.m., n=3, *P<0.05 via Student's t-test. miR, microRNA; 3'-UTR, 3'-untranslated region.