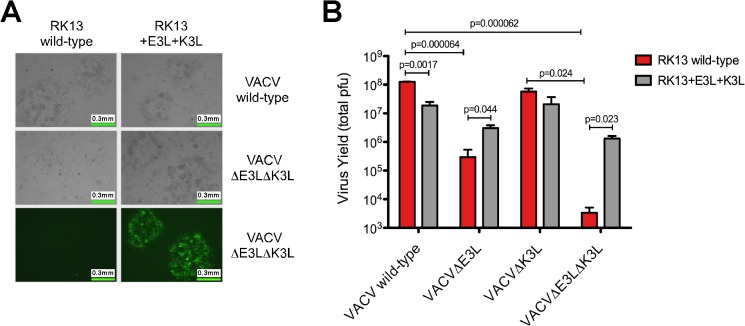
Fig 2. Growth of VACVΔE3LΔK3L is restored in RK13 cells expressing VACV E3 and K3 proteins.
(A) VACVΔE3LΔK3L was constructed using homologous recombination techniques and engineered to express GFP in place of the E3L gene. No plaque formation was visualized in wild-type RK13 cells whereas replication capacity was restored in RK13 cells stably expressing E3 and K3 proteins derived from VACV. Representative images are shown. (B) The total yield of VACV wild-type, VACVΔE3L, VACVΔK3L, and VACVΔE3LΔK3L was determined using wild-type RK13 (red bars) and RK13+E3L+K3L (gray bars) cells. Cells were initially infected with a low amount of virus (MOI = 0.01). Virus was harvested 30 hours post-infection and the total yield was determined using standard plaque assays with RK13+E3L+K3L cells. The data is the average of two independent experiments with error bars representing the standard deviation. P-values were determined in Microsoft Excel using the Student’s t-test.