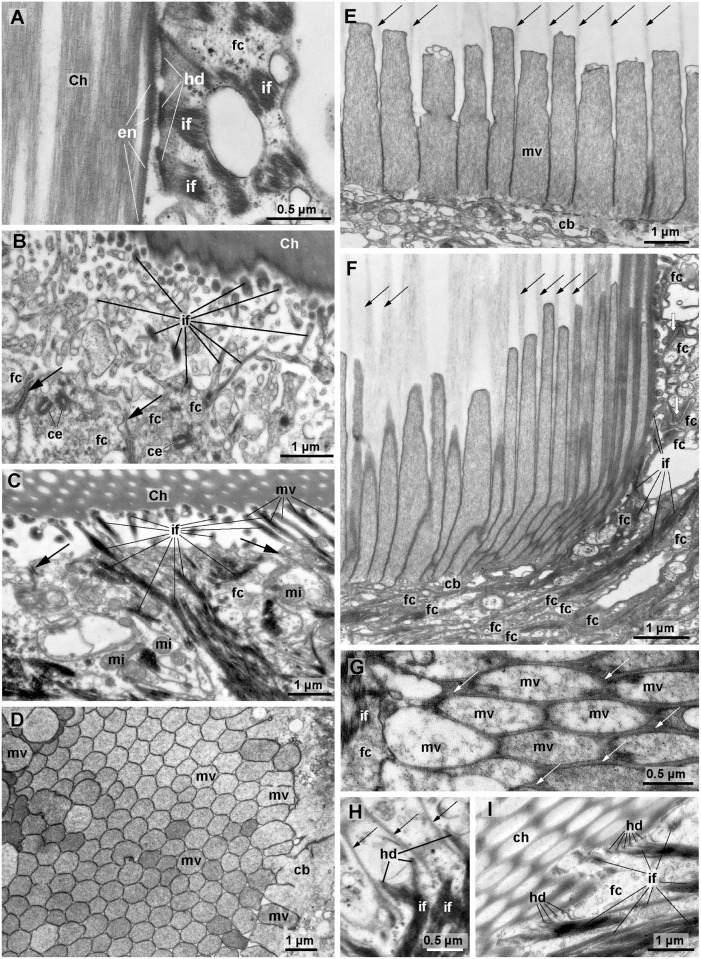
Fig 4. Ultrastructure of ventral chaetae of Echiurus echiurus (A, D-F) and Thalassema thalassemum (B, C, G-I), TEM.
A-G. late chaetogenesis, H-I. complete chaeta. A. Hemidesmosomes (hd) connect chaeta (Ch) to intermediate filaments (if) of follicle cells (fc), chaeta is surrounded by an enamel (en). B, C. Intermediate filaments (if) inside branched and unbranched microvilli (mv) adhere chaeta to follicle cells (fc). Apical adherens junctions (arrows) interconnect follicle cells, note apical pair of centrioles (ce) in follicle cells in B. D. Semi-transverse section of microvilli (mv) brush border of a chaetoblast (cb) during chaetogenesis. E, F. Parasagittal section of chaetoblast with apical microvilli, arrows mark chitin polymerizing between the microvilli. Note densely packed f-actin in microvilli (mv). E. center of chaetoblast. F. lateral part of chaetoblast. Note its tight interdigitation with follicle cells (fc), white arrows mark adherens junctions. G. Semi-transverse section of apical microvilli of the chaetoblast, white arrows mark chitin polymerizing between the microvilli (mv). H. Base of old chaeta, parasagittal section. The apical microvilli have been replaced by protrusions of the chaetoblast that contain intermediate filaments (if) which adhere to the chaeta (arrows) by hemidesmosomes (hd). I. Fully differented chaeta with ridges. Hemidesmosomes (hd) firmly connect intermediate filaments (if) of follicle cells (fc) to chaeta. mi mitochondria.