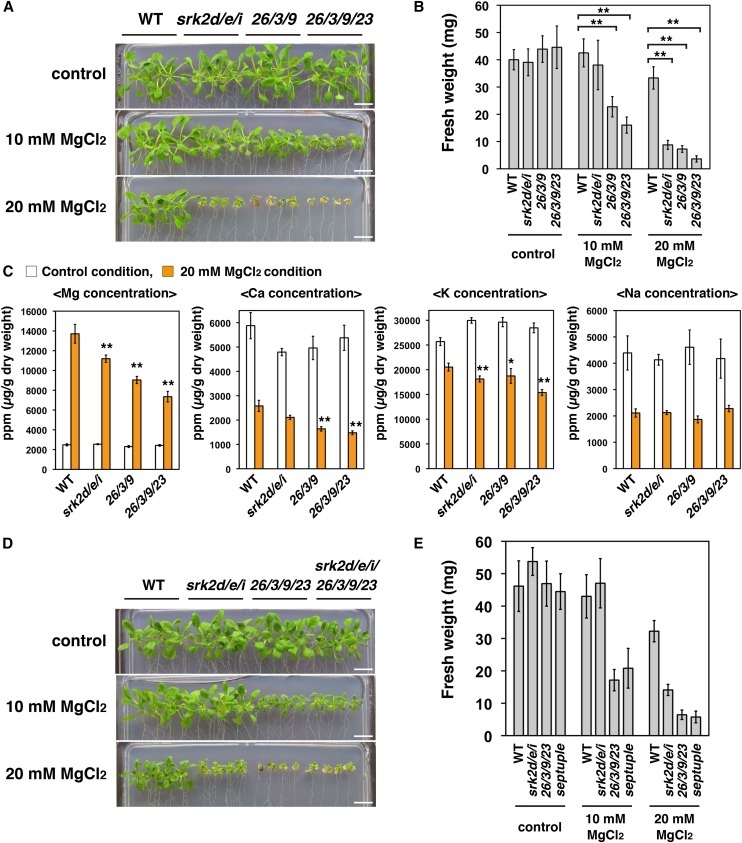
Figure 5.
The srk2d/e/i triple mutant shows increased susceptibility to a high external Mg2+ concentration. A, Growth phenotypes of the wild type, srk2d/e/i and cipk26/3/9 triple mutants, and the cipk26/3/9/23 quadruple mutant grown under a high external Mg2+ concentration. Photographs show representative phenotypes of 18-d-old seedlings grown vertically for 4 d on GM plates and then for 14 d on one-half-strength Murashige and Skoog medium agar plates containing indicated concentrations of MgCl2. Bars = 1 cm. B, Fresh weight of seedlings treated as described in A. Similar results were obtained in independent experiments; representative data are shown. Bars indicate sd (n = 8). Asterisks indicate statistically significant difference. **, P < 0.01, two-way ANOVA followed by a post hoc Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison test. C, ICP-MS analyses of magnesium, calcium, potassium, and sodium concentrations in aerial parts of plants grown vertically for 4 d on GM plates and then for 12 d on one-half-strength Murashige and Skoog agar plates with or without the addition of 20 mm MgCl2. For each biological replicate, material from four plants was pooled to make one sample for ICP-MS analysis. Data represent means and sds (n = 6). Orange bars, 20 mm MgCl2; white bars, control. Asterisks indicate that the corresponding mean is significantly different from the mean value of the wild type within each condition. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, two-way ANOVA followed by a post hoc Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison test. D, Susceptibility of the srk2d/e/i/cipk26/3/9/23 septuple mutant to high external Mg2+ concentrations. Plants were grown as described in A. Bars = 1 cm. E, Fresh weight of seedlings treated as described in D. Similar results were obtained in independent experiments; representative data are shown. Bars indicate sd (n = 8). WT, Wild type.