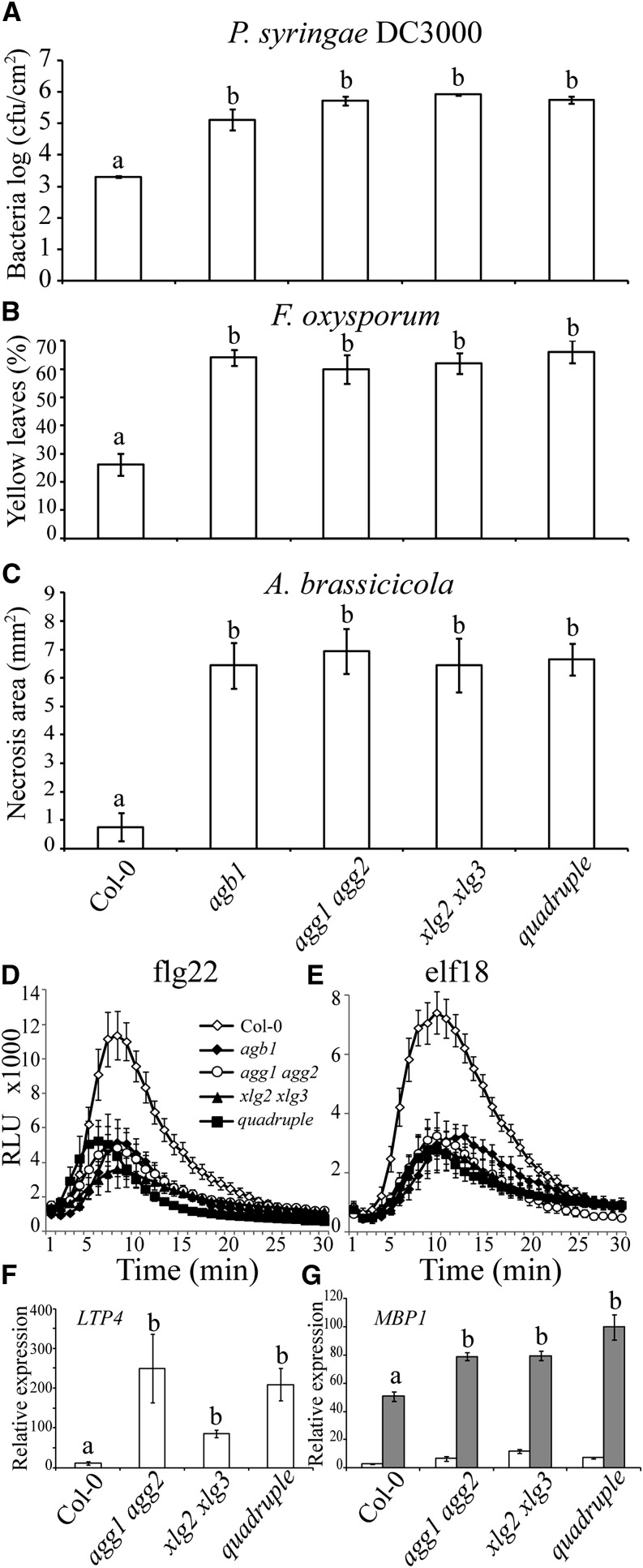
Figure 2.
XLGs and Gβγ act in the same signaling pathway to elicit the defense response. A, Bacterial growth of Pst DC3000 at 3 dpi. Five-week-old plants were spray inoculated with the bacterium (OD600 = 0.4). Three plants per genotype (seven leaf discs per sample) were harvested to measure bacterial titer. B, Percentage of yellow leaves 6 d after F. oxysporum inoculation of 3-week-old plants (n = 20). C, Area of necrotic lesion development in response to A. brassicicola drop inoculation at 5 dpi. Five-week-old plants (n = 10) were assayed. D and E, ROS production in response to PAMP treatment including 1 µm flg22 (D) and 1 µm elf18 (E). Relative luminescence units (RLU) was plotted against time (min). Leaf discs of 5-week-old plants (n = 12) were used. F and G, Defense-related gene expression in quadruple mutants compared with their parental mutants. Three-week-old plants were harvested for total RNA extraction (n = 3). Three biological replicates were used for quantitative real-time PCR. F, Steady-state expression levels of LTP4 in uninfected plants. G, Pathogen-induced expression levels of MBP1. Plants were inoculated with F. oxysporum (gray bars) or mock inoculated (white bars). Samples were collected at 3 dpi. In all sections, wild-type Col-0 and agg1 agg2 double, xlg2 xlg3 double, and agg1 agg2 xlg2 xlg3 quadruple mutants were studied. For A to E, agb1 mutant was included for comparison. The dataset represents mean ± sem. Experiments were repeated twice with similar results. For A to C and F and G, the letters represent groups of statistically significant differences based on one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison method. A difference between each group represents P < 0.001 (A), P < 0.0001 (B and C), and P < 0.01 (F and G). cfu, Colony forming units.