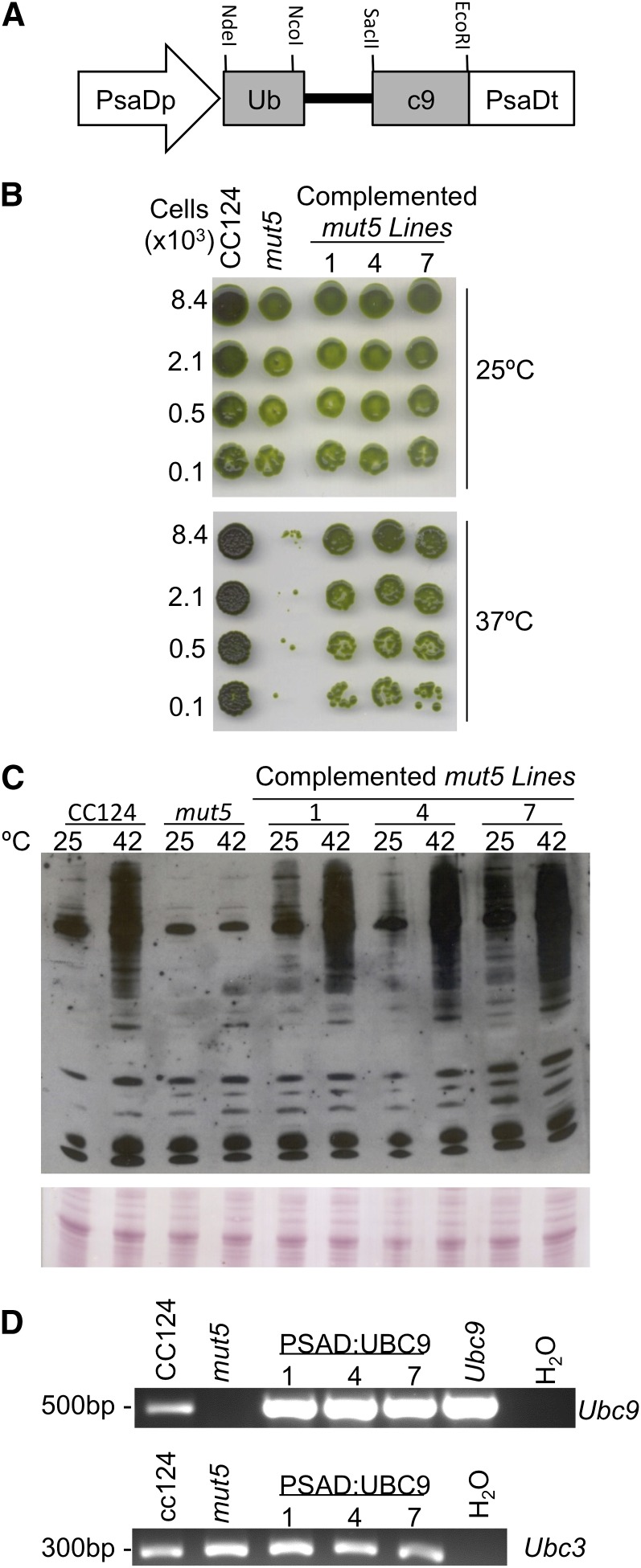
Figure 5.
Complementation of mut5 with CrUBC9. A, Diagram of the pGenD-Ubc9.int2 expression cassette. Shown are NdeI and EcoRI sites used for cloning CrUbc9 cDNA between the C. reinhardtii PsaD gene promoter and terminator regions in the pGenD vector as well as endogenous NcoI and SacII sites used for adding the second intron of the CrUBC9 gene. B, mut5 lines 1, 4, and 7 putatively complemented with the CrUBC9 gene construct pGenD-Ubc9.int2 were screened for their ability to grow at 37°C. Normalized cell cultures of wild-type, mut5, and complemented lines were spotted on two TAP plates, one of which was incubated at 25°C as a control and one of which was incubated at 37°C for 3 d before shifting to 25°C to assess growth. C, Putative complemented lines were tested for the ability to SUMOylate proteins in response to 42°C. Cell cultures were shifted to 42°C for 1 h, and whole-cell extracts were analyzed for SUMOylation by immunoblot with anti-SUMO antibodies. D, Confirmation of the expression of CrUBC9 in complemented lines by RT-PCR analysis. RNA was isolated from wild-type, mut5, and complemented lines. RT-PCR using CrUbc9-specific primers was used to detect the production of CrUbc9 transcripts. The next to last lane contains the product from RT-PCR amplification of a cDNA clone of CrUBC9. Expression of CrUbc3 was used as a control. Lanes marked H2O are negative controls with no template RNA added.