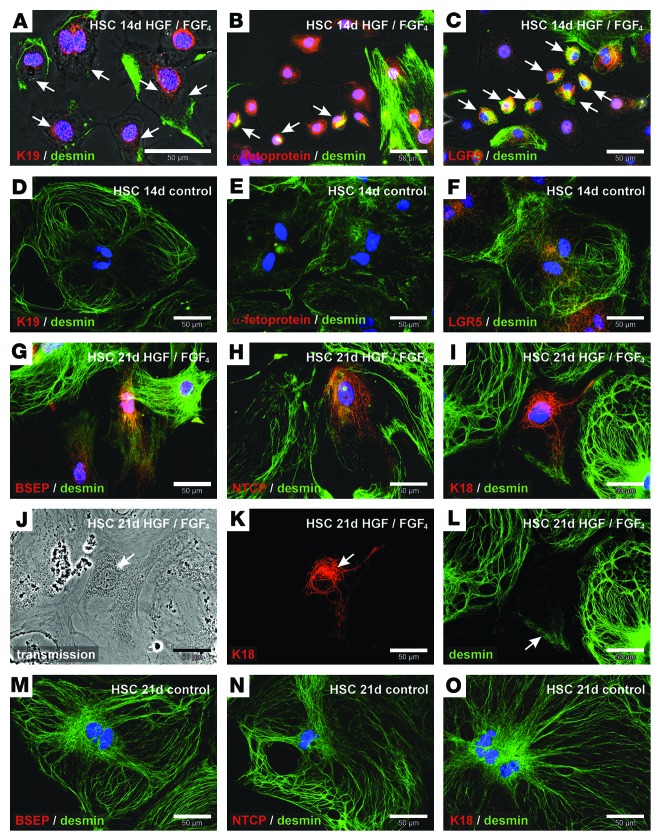
Figure 8. Isolated HSCs form intermediate states of mesenchymal and epithelial cells during differentiation into hepatocyte-like cells.
Combined immunofluorescence of (A) K19 and (B) α-fetoprotein as well as (C) LGR5 (red) with the mesodermal filament protein desmin (green) after treatment of primary HSC cultures with HGF and FGF4 for 14 days. Small cells with K19, α-fetoprotein, or LGR5 that coexpressed desmin are indicated with arrows. HSCs without growth factors (control) were also analyzed by immunofluorescence of (D) K19, (E) α-fetoprotein, or (F) LGR5 (red) in combination with desmin (green) after 14 days of culture. Hepatic differentiation of HSCs was analyzed by immunofluorescence of (G) BSEP, (H) NTCP, and (I) K18 (red) after 21 days of growth factor treatment. (G–L) To investigate the relationship of newly formed hepatocyte-like cells with HSCs, desmin residues were stained by immunofluorescence (green). (J) Transmission light microscopy and single immunofluorescence channels of (K) K18 (red) and (L) desmin (green) of the hepatocyte-like cell shown in I. Combined immunofluorescence analysis of (M) BSEP, (N) NTCP, and (O) K18 (red) with desmin (green) was also performed in HSCs cultured for 21 days without growth factor treatment (control).